Figure 8.
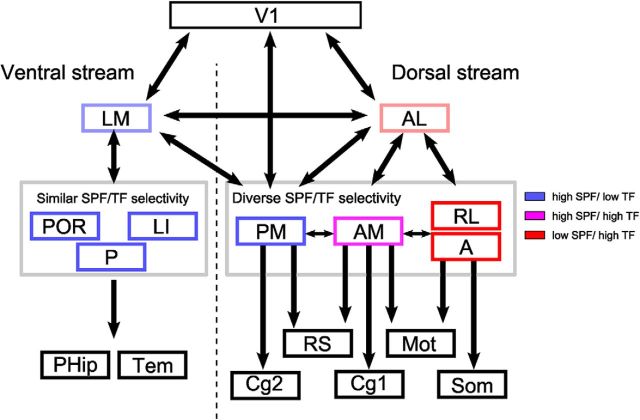
Summary of the anatomical (Wang et al., 2012) and functional streams of mouse HVAs. The schematic of visual streams is based on Wang et al. (2012). The putative ventral stream consists of four lateral HVAs (LM, LI, POR, and P) (Wang et al., 2012). Area LM is considered as a gateway to the putative ventral stream and areas LI, P, and POR send projections to parahippocampal (PHip) and temporal cortices (Tem) (Wang et al., 2011, 2012). These ventral HVAs share similar spatiotemporal selectivity (Fig. 3D,E) and this stream may process the pattern-related visual features for object recognition. The putative dorsal stream consists of anterior/medial HVAs (AL, PM, AM, RL, and A) (Wang et al., 2012). Area AL is considered to be a gateway to the putative dorsal stream (Wang et al., 2011). The current study indicates that the spatiotemporal selectivity of the remaining four HVAs is not uniform and these areas form three functionally distinct groups (Fig. 3D,E) that have different anatomical targets (Wang et al., 2012). The first group, area PM, has strong connections to the RS and Cg2 areas. The second group, area AM, sends strong projections to the motor (Mot) and Cg1 areas. Finally, the third group, areas RL and A, sends strong projections to the somatosensory (Som) and motor cortices.