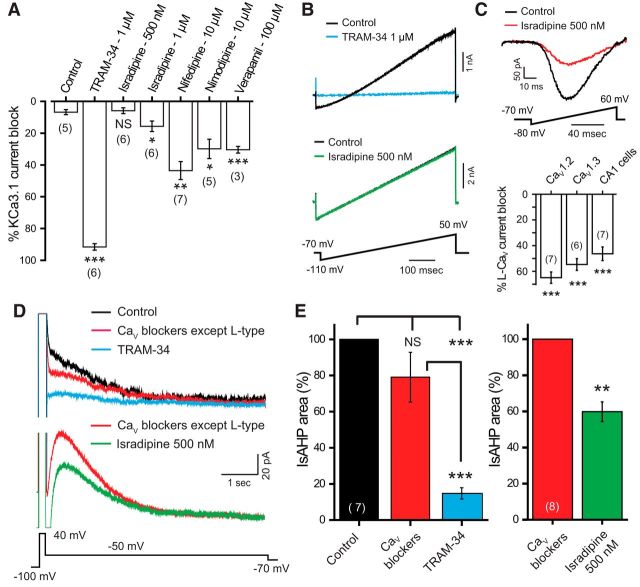
Figure 5.
L-type channels play a key role in evoking the CA1 pyramidal cell IsAHP. A–C, The effects of L-type calcium channel blockers on KCa3.1 whole-cell current recorded in tsA-201 cells with 1 μm calcium in the electrode and evoked by a ramp command as shown in B. Bar plots show a differential block of KCa3.1 current by L-type blockers (A). Representative recordings of KCa3.1 current in B and C illustrate a complete block by 1 μm TRAM-34 but no effect of 500 nm isradipine, a dose sufficient to provide substantial block of whole-cell L-type calcium current in tsA-201 cells expressing either CaV1.2 or CaV1.3 cDNA or in CA1 pyramidal cells (C). D, E, The IsAHP in rat CA1 hippocampal pyramidal cells evoked by a depolarizing step command of 200 ms to 40 mV. The IsAHP is only slightly reduced by a medium containing blockers against all CaV channels except L-type (1 μm ω-conotoxin MVIIC, 200 nm ω-agatoxin IVA, 200 nm SNX-482, 1 μm TTA-P2). The remaining presumed L-type channel-activated IsAHP is significantly reduced by 1 μm TRAM-34. Recordings in the bottom part of D are from a separate cell in which 500 nm isradipine was applied in the presence of the non-L-type CaV channel blockers, revealing a significant reduction of IsAHP. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. NS, Not significant. Cell numbers are shown in brackets in A, C, and E.