Figure 2.
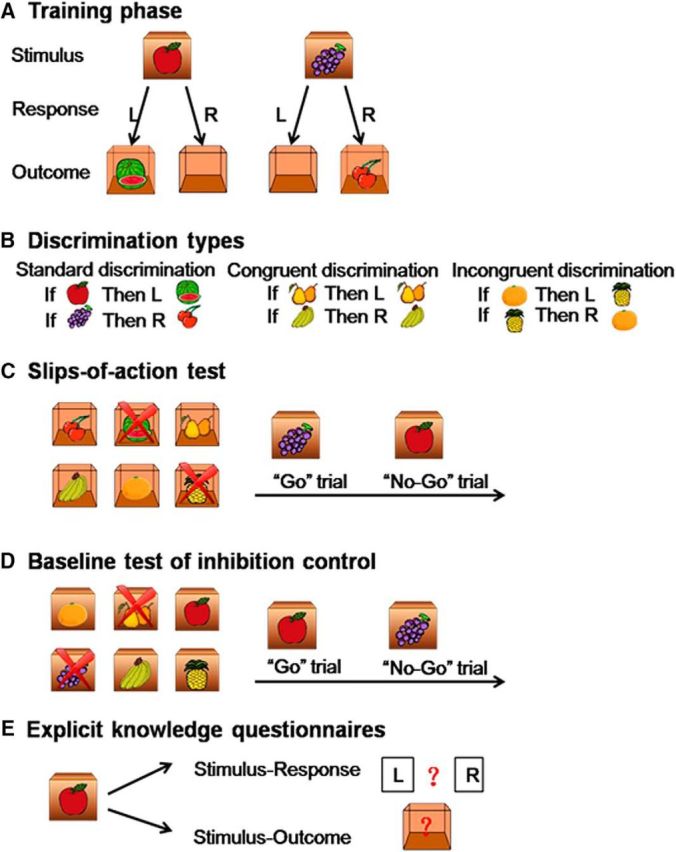
Instrumental learning task description. A, The training phase. Participants were shown various closed boxes with one kind of fruit (i.e., the stimulus) on the outside of each box. They were required to press the correct key (left key or right key, i.e., the response) to open the box, and obtain another fruit (i.e., the outcome) inside the box and subsequently earn points. If the response was incorrect, an empty box was shown with no points given. Participants learned the stimulus-outcome-response associations by trial and error. B, Three discrimination types (standard, congruent, and incongruent discriminations) were used for this task. C, The slips-of-action test. This test directly assessed the balance between goal-directed and habitual learning systems. First, six open boxes with outcomes inside were shown, two of which were marked with crosses. These two outcomes would lead to the subtraction of points, and participants should withhold any response to the corresponding stimuli (No-Go trials), whereas the other four outcomes were valuable and participants should make the correct response (Go trials). D, Baseline test of inhibition control. This was a control test of slips-of-action test for general inhibitory impairments. First, six closed boxes with stimuli onside were shown, two of which were marked with crosses. These two stimuli would lead to the subtraction of points and participants should withhold any response to these two boxes (No-Go trials), whereas the other four stimuli were valuable and participants should make the correct response (Go trials). E, Explicit knowledge questionnaire. Participants were examined on the corresponding response and outcome for each stimulus with paper-and-pencil questionnaires.
