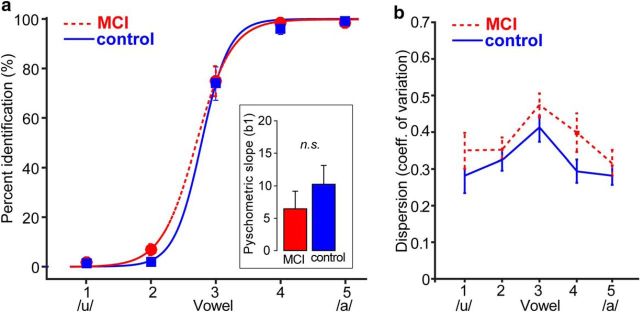
Figure 1.
Behavioral speech listening skills are similar in MCI and control listeners. Shown are behavioral identification (a) and variability (CVs) in RTs (b) for speech identification in normal and MCI listeners. a, Psychometric identification functions illustrate the proportion of trials categorized as one of two phonetic classes (/u/ or /a/) across a vowel continuum. Inset shows the slope of psychometric functions estimated from the sigmodal fit. No group differences were observed in psychometric slopes. b, MCI and control listeners labeled speech tokens with similar average variability, as evident by the CV of the RTs. Error bars indicate ±1 SEM.