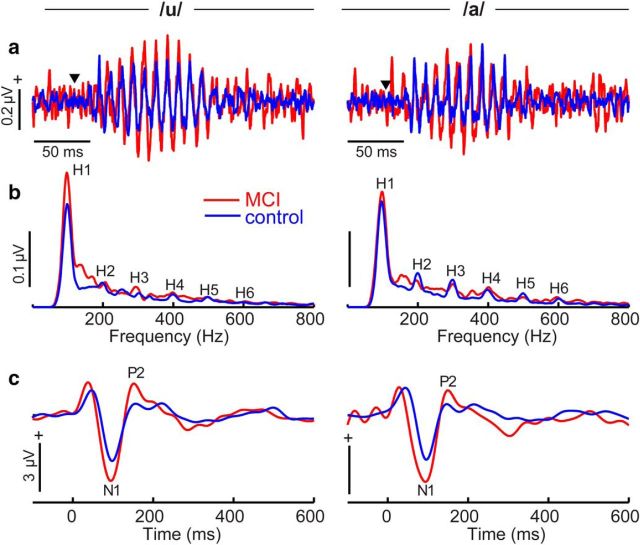
Figure 3.
Neuroelectric brain activity reveals deficient speech coding at subcortical and cortical levels in MCI. a, b, Brainstem FFR time waveforms (a) and spectra (b) illustrating responses to the two prototypical vowel tokens /u/ (vw1) and /a/ (vw5). Time waveforms show phase-locked neural activity from the brainstem. ▾ indicates the onset of the time-locking speech stimulus. MCI FFRs are characterized by an increase in amplitude that is largely attributed to hypersensitive coding of the vowel's fundamental frequency (H1 = 100 Hz) and integer-related harmonics (H2–H6). c, Cortical ERPs to speech. As with brainstem FFRs, MCI shows aberrant neural speech coding at the cortical level as indicated by overexaggerated N1–P2 magnitudes.