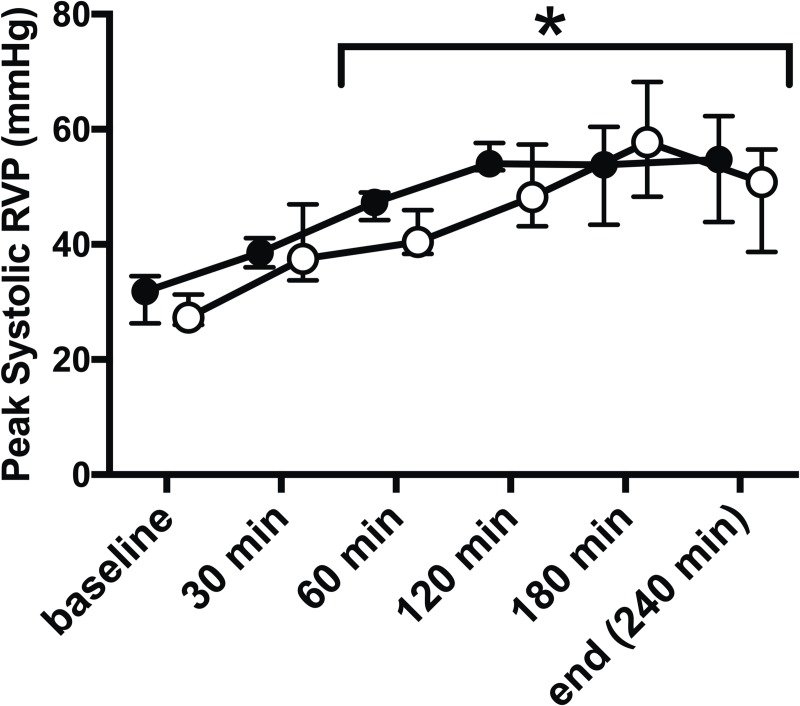
Fig 1. E. coli infusion increases RV pressure, which was mimicked by pulmonary artery banding.
Infusion of E. coli (filled circles) caused significant increase of peak systolic right ventricular pressure (RVP) assessed by RV manometer surveillance at 60 min and throughout the remaining study period (*, p < 0.01). Manual external pulmonary artery banding (open circles) mimicked these changes with similar and significant RVP increase after 30 min and was at no time-point during the study significantly different from E. coli induced peak systolic RVP. All values Median ± Interquartile Range. Generalized linear mixed model with post-hoc comparison to baseline and pairwise comparison between pulmonary artery banding and sepsis at each time-point. Bonferroni correction for multiple testing.