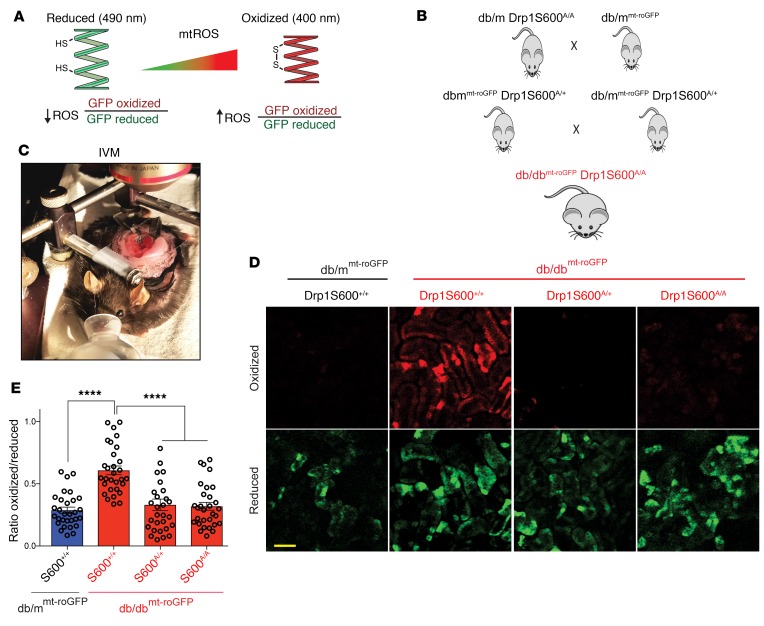
Figure 4. Mitochondrial redox–sensitive roGFP indicates that the Drp1S600A attenuates mtROS in the kidneys of live diabetic mice.
(A) Cartoon depicting the principles of ratiometric redox-sensitive mt-roGFP. CMV-driven expression was localized to the mitochondrial matrix using a cytochrome oxidase subunit IV–signaling (COX IV–signaling) sequence. The oxidation state of the engineered thiols determines the fluorescence properties of the sensor, which shifts depending on the oxidized, disulfide-bonded glutathione/reduced glutathione (GSSG/GSH) equilibrium. Cysteine sulfhydryl groups are illustrated, HS, free sulfhydryl; SS, disulfide bonded. (B) Generation of db/dbroGFP Drp1S600A/A mice allows for monitoring of mitochondrial redox status in the kidneys of live Drp1S600-knockin mice. (C) Image of IVM setup. (D) Ratiometric changes in the fluorescence intensity obtained at the oxidized excitation wavelength (red) and the reduced excitation wavelength (green). Scale bar: 100 μm. (E) Ratiometric quantitative analysis from intravital images, in which oxidized fluorescence is placed as the numerator and reduced fluorescence as the denominator. Representative images are from a sampling of 3 animals. ****P < 0.0001, by 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. Results are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 3 mice/group).