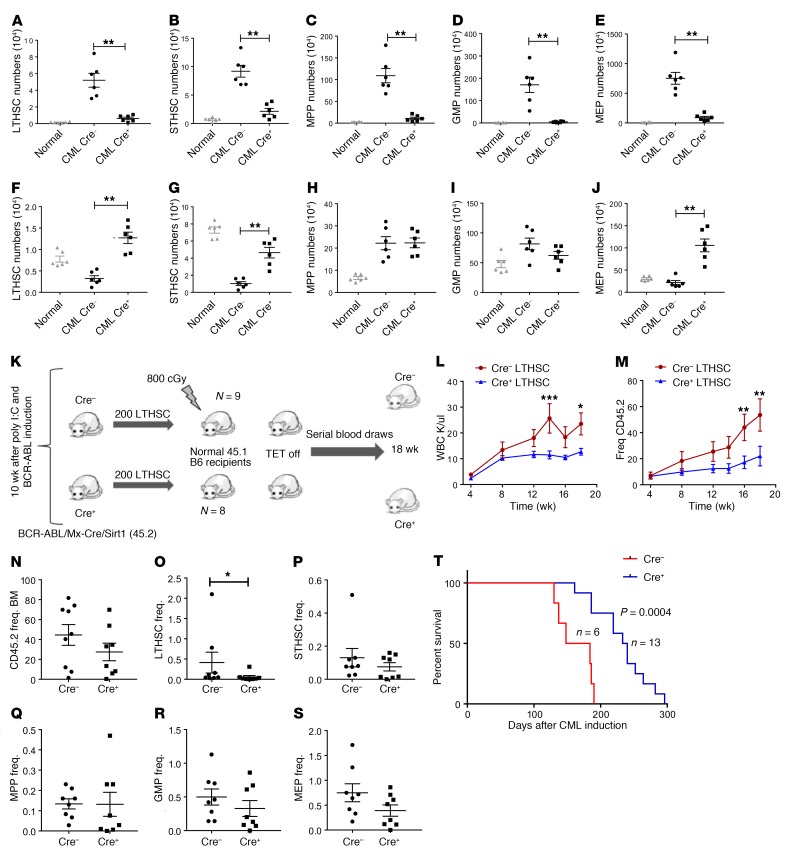
Figure 3. Mx1-Cre–mediated SIRT1 deletion inhibits CML stem and progenitor cells.
(A–E) Effect of SIRT1 deletion on splenic stem and progenitor subpopulations, including LTHSCs (A), STHSCs (B), MPPs (C), GMPs (D), and MEPs (E), at 8 weeks after SIRT1 deletion (n = 6 each). (F–J) Effect of SIRT1 deletion on BM stem and progenitor subpopulations, including LTHSCs (F), STHSCs (G), MPPs (H), GMPs (I). and MEPs (J). Corresponding stem and progenitor cell populations from normal mice are shown for comparison. (K) Experimental strategy for checking long-term repopulating potential of LTHSCs following SIRT1 deletion. Donor LTHSCs (CD45.2) were selected from SIRT1-deleted and control primary recipient mice by flow cytometry and transplanted to sublethally irradiated (800cGy) secondary recipients (200 cells/mouse), together with 500,000 supporting BM cells (CD45.1) (n = 8–9 each). (L–S) Recipient mice were followed with serial blood counts and subsequently analyzed for BM stem and progenitor cells. Peripheral blood WBC counts and frequency of CD45.2 donor cells (M) in secondary recipients are shown. (N–S) Frequency (Freq.) of donor cells, including total CD45.2 (N), LTHSCs (O), STHSCs (P), MPPs (Q), GMPs (R), and MEPs (S) in secondary recipient BM. (T) Kaplan-Meier analysis of survival of SCL-tTA/BCR-ABL Mx1-Cre SIRT1fl/fl mice compared with Cre controls. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, t test, except Kaplan-Meier analysis.