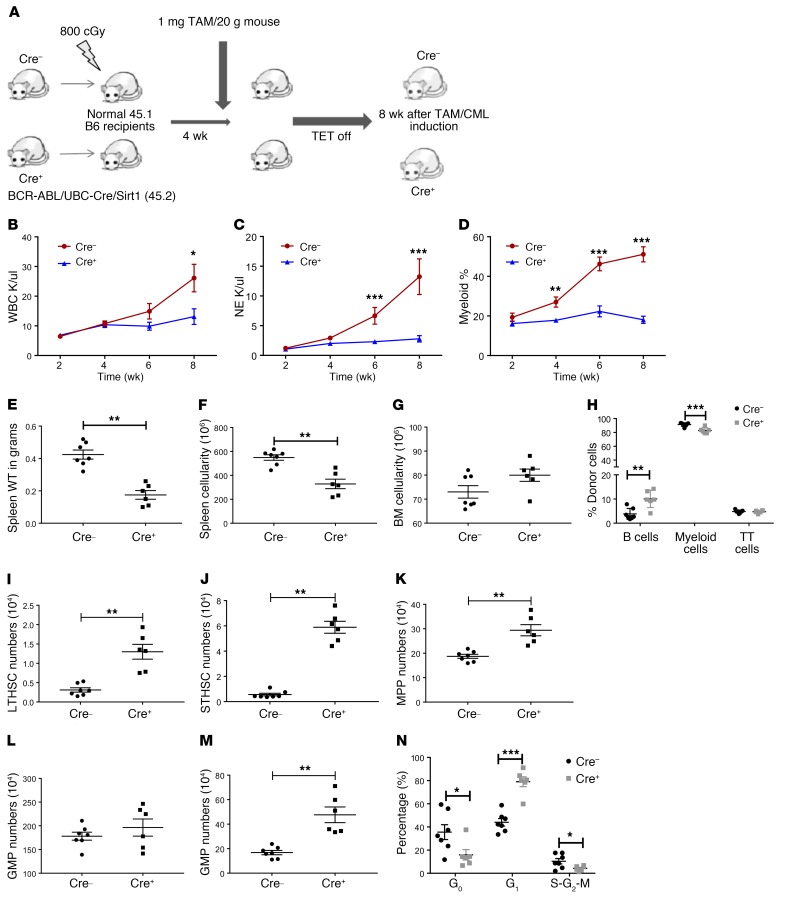
Figure 4. UBC ERT2-Cre–mediated SIRT1 deletion inhibits CML hematopoiesis.
(A) Experimental strategy for studying the effect of SIRT1 deletion on CML development using UBC ERT2-Cre/SIRT1fl/fl/BCR-ABL model: BM cells from either SCL-tTA-BCR-ABL UBC-ERT2-Cre SIRT1fl/fl or Cre– controls (both CD45.2) were transplanted into irradiated (800 cGy) CD45.1 congenic recipients (2 × 106 cells/mouse). Cre-mediated deletion of SIRT1 was induced by tamoxifen (TAM) injection (1 mg/mouse) starting at 4 weeks after transplant, followed by tetracycline withdrawal to induce BCR-ABL expression. Mice were sacrificed and analyzed 8 weeks after CML induction and SIRT1 deletion (n = 10 each). (B–D) Effect of SIRT1 deletion on blood parameters, including WBC (B), neutrophil counts (C), and donor Gr1+Mac1+ myeloid cell frequencies determined by flow cytometry (D) (n = 6–7). Effect of SIRT1 deletion on spleen weight (E), spleen cellularity (F), BM cellularity (G), and frequencies of donor B cells, myeloid cells, and T cells in BM by flow cytometry (H) at 8 weeks. (I–M) Effect of SIRT1 deletion on absolute numbers of BM LTHSCs (I), STHSCs (J), MPPs (K), GMPs (L), and MEPs (M). (N) Cell cycle analysis on LTHSC populations from BM using DAPI and KI67 labeling. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, t test.