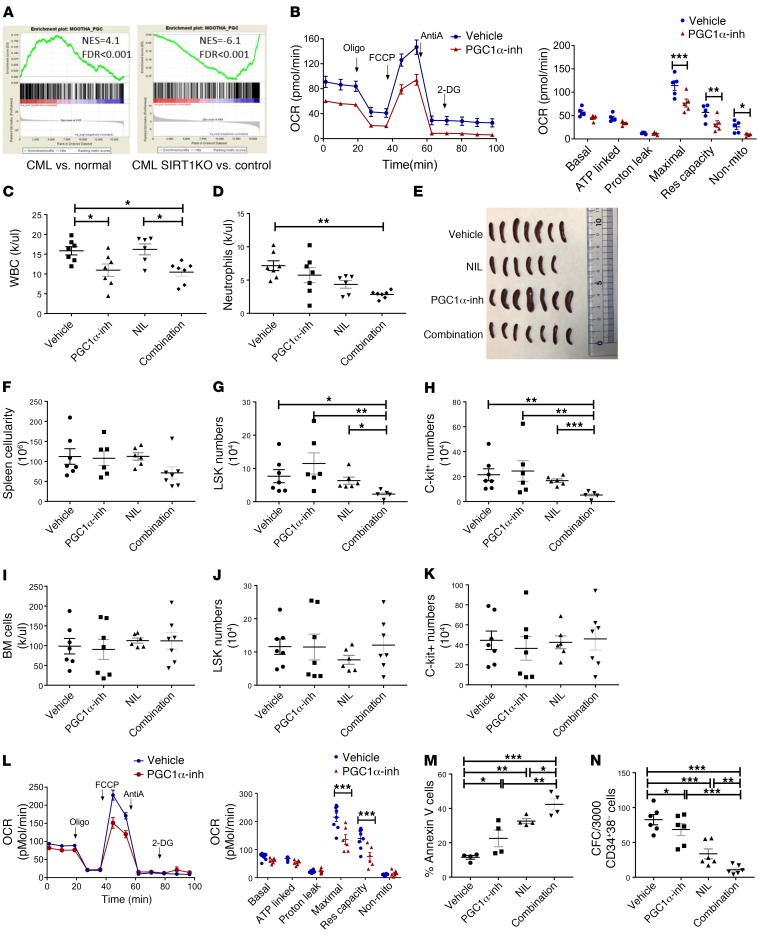
Figure 9. PGC-1α regulates mitochondrial metabolism and contributes to TKI resistance in CML stem/progenitor cells.
(A) GSEA analysis of gene expression data shows enrichment of the PGC-1α–related gene set in LTHSCs obtained from CML mice compared with normal mice and downregulation in LSK cells from SIRT1-deleted compared with control Cre– CML mice. (B) OCR measurements in c-Kit+ cells from CML mice treated with PGC-1α inhibitor (PGC-1α inh) (SR18292) or vehicle (n = 7 each) for 2 weeks. (C–E) CML mice were treated with vehicle, NIL, PGC-1α inhibitor, or combination (n = 7–8) for 2 weeks. The effect of treatment on WBC (C), neutrophil counts (D), spleen size (E), spleen cellularity (F), splenic LSK cells (G) splenic c-Kit+ cells (H), BM cellularity (I), BM LSK cells (J), and BM c-Kit+ cells (K) are shown. (L) Measurement of OCR in CML CD34+ cells (n = 3) treated with PGC-1α inhibitor or vehicle overnight. (M) Apoptosis of CML CD34+CD38– cells (n = 3) treated with vehicle, PGC-1α inhibitor, NIL, or combination for 72 hours, measured by annexin V labeling. (N) Colony formation from CML CD34+CD38– cells (n = 3) exposed to vehicle, PGC-1α inhibitor, NIL, or combination for 48 hours and plated in methylcellulose progenitor culture. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, ordinary 1-way ANOVA (M and N), Kruskal-Wallis 1-way ANOVA (C–K), or 2-way ANOVA (B and L), correcting for multiple comparisons by controlling the FDR using the 2-stage linear step-up procedure of Benjamini, Krieger, and Yekutieli.