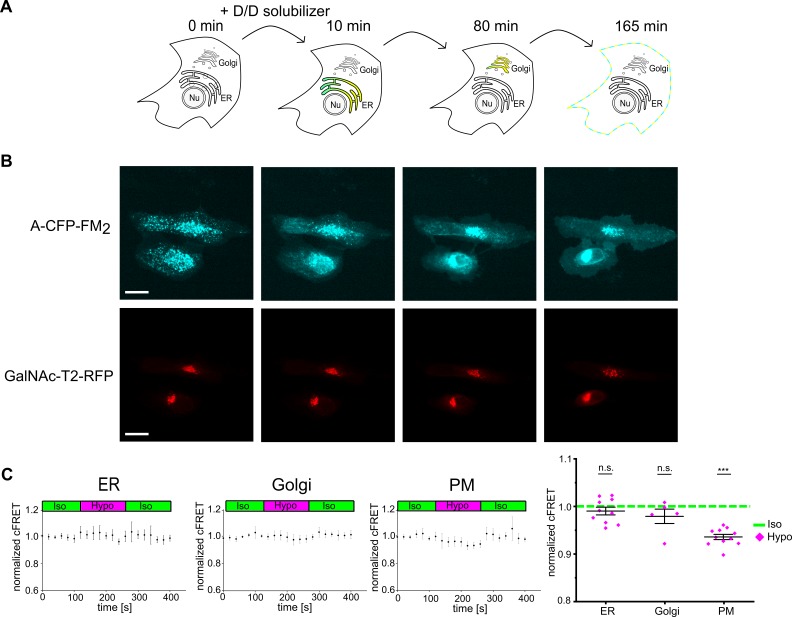
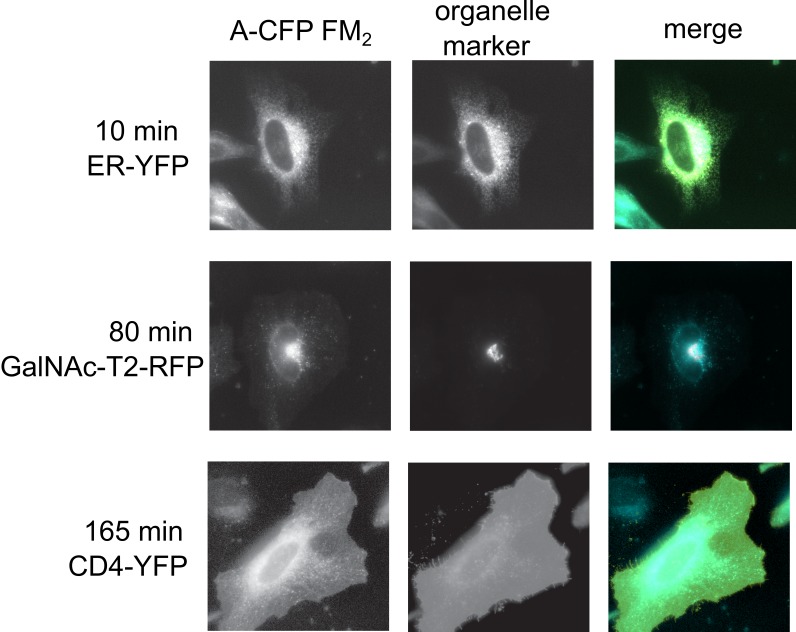
Figure 3. Plasma membrane localization is required for VRAC activation.
(A) Scheme depicting the different subcellular localizations of VRACs using the reverse aggregation system. Upon addition of the D/D solubilizer, VRACs carrying FM dimerization domains disaggregate in the ER and travel through the Golgi complex to the plasma membrane. Indicated time points were deduced from experiments shown in (B) and (Figure 3—video 1). (B) Still images of HeLa cells expressing LRRC8A-CFP-FM2 and GalNAcT2-RFP as Golgi marker from Figure 3—video 1 at time points indicated in (A). Scale bar, 20 µm. (C) cFRET measured in HeLa cells expressing A-CFP-FM2/E-YFP. VRACs localizing to the ER (n = 4, 10 cells), Golgi (n = 5, 26 cells) and plasma membrane (PM; n = 5, 11 cells) were measured at 10, 80 and 165 min after addition of D/D solubilizer. Data in time traces represent mean ± s.d. Right: average normalized cFRET in of the first seven time points in isotonic and last three time points in hypotonic buffer. Data represent individual cells (ER, PM) or FOVs (Golgi) and mean ± s.e.m. Statistics: ***p<0.0005; n.s., not significant, Student’s t-test, comparing hypotonic with isotonic.