Figure 2. Normal and UV-induced redistribution during progression through the cell cycle in p53-competent human cells.
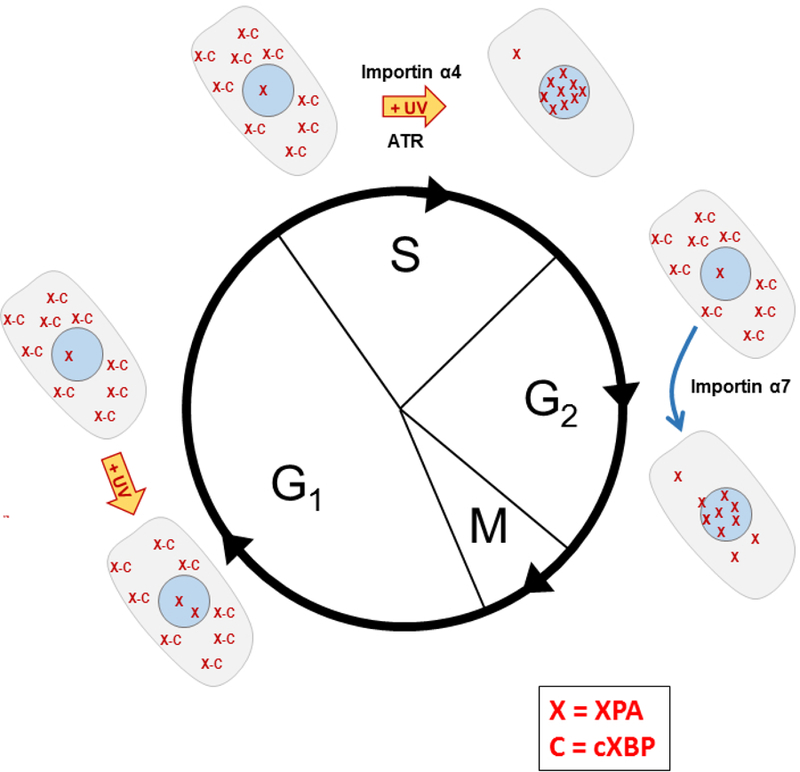
This model is based on the studies of Li et al. 68–70 In non-damaged cells in the G1 phase XPA (X) is mostly located in the cytosol, likely bound to cXBP (C), a hypothetical cytosolic XPA sequestration protein. Exposure of G1 cells to UV does not change this distribution. Likewise, in S phase cells XPA is mostly cytosolic; however, UV exposure induces a release of XPA from cXBP and a translocation of XPA into the nucleus. This XPA nuclear translocation in S phase requires the importin α4 transport protein and is ATR kinase- and p53-dependent in p53-competent cells. XPA is primarily located in the nucleus in G2 phase cells, transported there via importin α7 in a process independent of UV exposure. The XPA redistributes to the cytosol during the M-G1 phase transition and reassociates with cXBP.
