Figure 1.
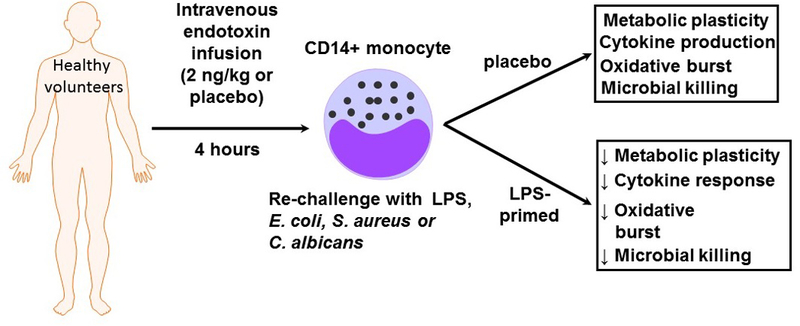
Endotoxin induced immunotolerant monocytes show a loss of metabolic plasticity and antimicrobial function. In this study, Grondman and colleagues administered endotoxin (2 ng/kg) or placebo to normal, healthy male volunteers in an ICU setting. CD14+ monocytes were harvested at 4 hrs and 7 days after endotoxin infusion and treated with microbial stimuli. At four hours after endotoxin infusion, immunotolerant CD14+ monocytes showed a loss of metabolic plasticity which correlated with decreased antimicrobial activity. The authors postulate that these findings may have important implications for our understanding of sepsis induced immune paralysis.
