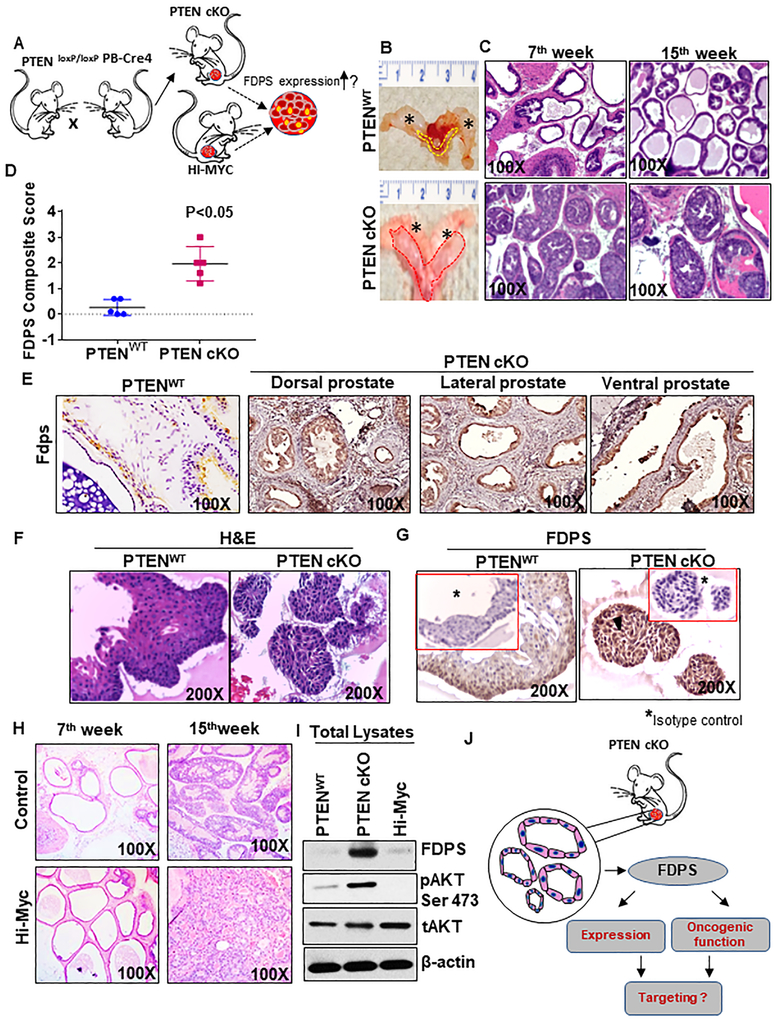
Fig. 1.
FDPS expression in prostate tissues and 3D organoid culture derived from normal and prostate cancer tissues of PTEN cKO mouse model. a Development of mouse models of prostate cancer to detect FDPS levels. PTEN cKO mouse model-derived prostate tissues, organoids and tumoroids were subjected to immunohistochemical analysis by staining with antibody specific for FDPS as indicated in material and methods. b Murine urogenital organs such as bladder, seminal vesicle and prostate were excised from 15 weeks old PTEN cKO and PTENWT control mice and examined for gross morphology. The asterix represents the seminal vesicle. Dotted lines show normal and enlarged prostate excised from the wild-type (yellow) and PTEN cKO (red) mice. c Histological analysis of mouse prostate cancer model. Representative images showing hematoxylin and eosin staining in mouse prostate dorsolateral lobes of PTENWT and PTEN cKO mice at 7 and 15 wks of age. d Box plot shows an increase in mean composite score of FDPS expression in mouse prostate of PTEN cKO mice compared with age-matched prostate tissues of PTENWT animal. e Immunohistochemical detection of FDPS protein in various lobes of mouse tissues. FDPS is highly expressed in epithelial cells of PTEN cKO prostate cancer tissues compared to PTENWT. f, g Representative image of a normal prostate organoid stained with hematoxylin and eosin (left) and FDPS antibody (right). g Positive immunoreactivity is shown for FDPS. Serial section of the same tumoroids and organoids used for FDPS staining were evaluated with non-specific isotype control antibodies (Insert). h Representative histological sections with hematoxylin and eosin staining of prostate tissues of wild-type (left) and Hi-Myc-driven transgenic mouse (right) at 7 and 15 wks of age. i Western blot analysis of FDPS, pAKT and total AKT expression in the total lysates isolated from prostates of 15 weeks old WT, PTEN cKO and Hi-Myc-driven mice. j Schematic diagram showing the application of tumoroids isolated from prostate-specific PTEN cKO mouse model to be used for FDPS expression analysis.