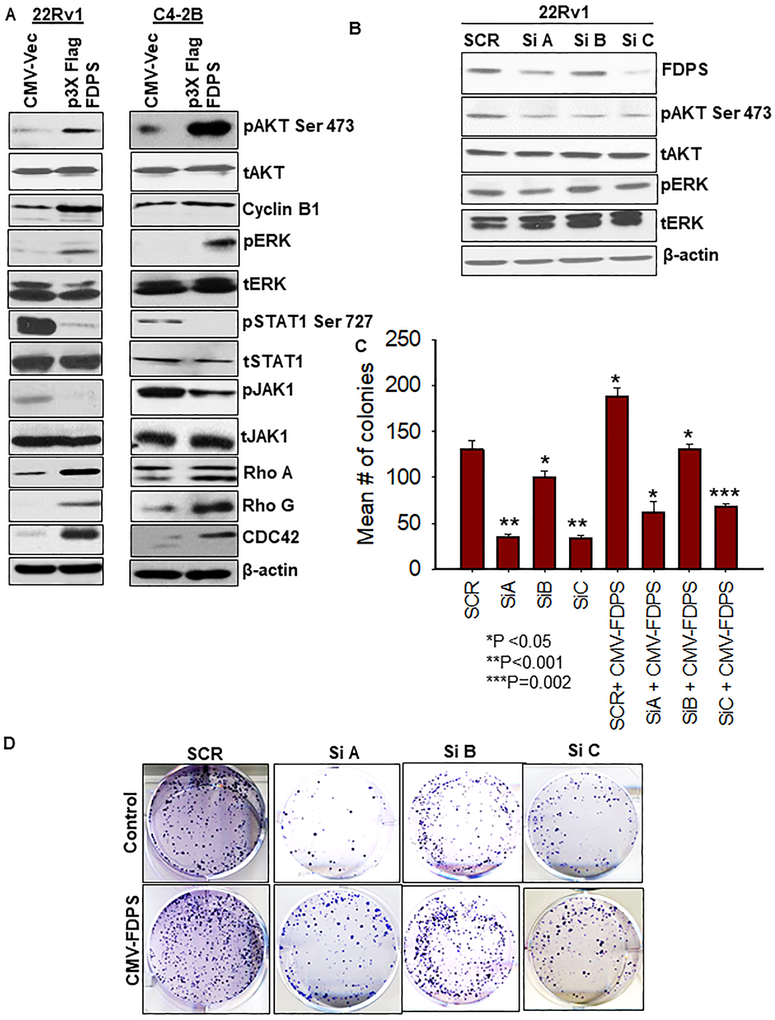
Fig. 4.
FDPS-mediated oncogenic signaling was more pronounced in PTEN-deficient prostate cancer cells than PTENWT cells. a The p3x-FLAG-CMV-10-FDPS and CMV-10 vector-transduced cells were seeded at a density of 1×106 in a 60 mm dish and analyzed for signaling molecules (AKT, ERK, JAK1/STAT1 and FDPS) with respective phospho forms by Western blot. Beta actin served as an internal loading control. Immunoblot analysis detected the un-prenylated and prenylated forms of RhoA, Rho G and CDC-42 proteins. Top band is the un-prenylated form and bottom band represents the prenylated proteins. b PCa cells were transiently transfected with 3 siRNAs targeting FDPS. After 48 h transfection, cell lysates were harvested and analyzed using Western blot for expression of FDPS, phosphoAKT, and ERK with respective total forms. c Effect of gene silencing of FDPS on clonogenicity was tested in 22Rv1 PCa cells. Bars represent the average number of colonies in siRNA-transfected cells, relative to scramble siRNA-transduced cells (N=3/group). d Representative images depict the reduction in the number colonies upon FDPS knockdown.