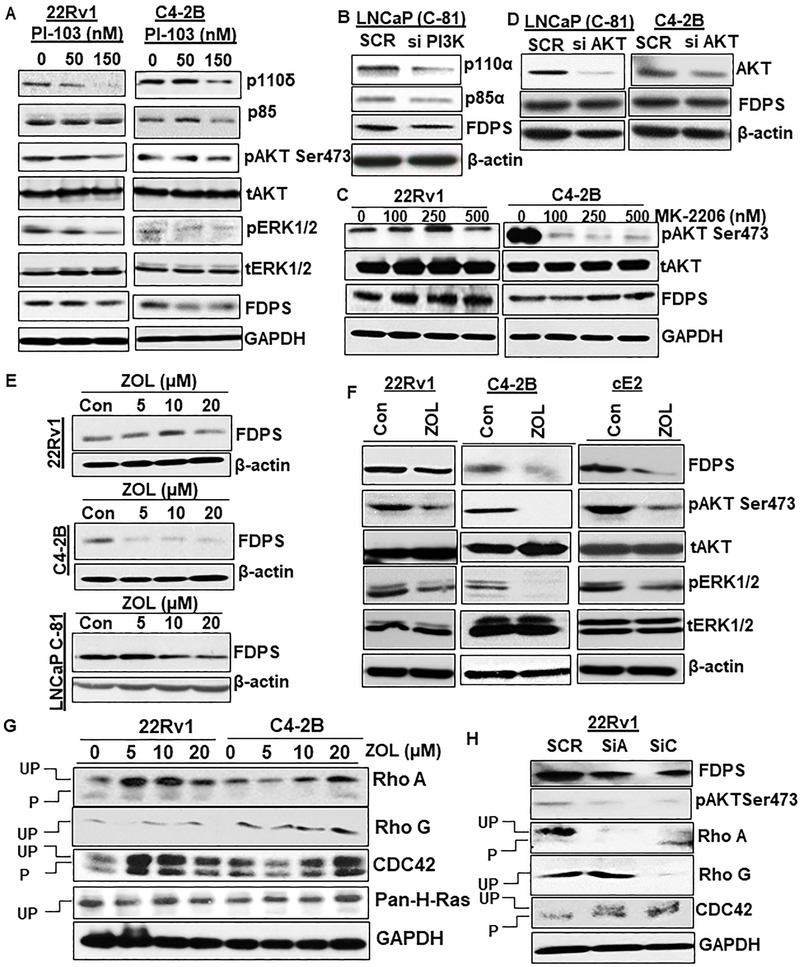
Fig. 5.
Pharmacological and genetic inhibition of PI3K or FDPS affects small GTPases/AKT axis. a and b PTEN-deficient C4-2B and PTEN-sufficient 22Rv1 cells were treated with and without PI3K-specific PI-103 or PI3K specific siRNA for 24 and 72 hr, respectively. Total lysates were immunoblotted and probed with PI3K subunits anti-p110α, anti-p110δ and anti-p85, anti-phospho AKT, anti-phospho ERK and anti-FDPS antibodies. c, d Effect of AKT specific MK-2206 inhibitor or siRNA alone treatment in PCa cells. e Dose-dependent effect of ZOL on 22Rv1, C4-2B and LNCaP C-81 PCa cells. After 48 hr exposure to ZOL, cells were lysed and subjected to Western blot to detect FDPS protein expression. ZOL induces a dose-dependent decrease in FDPS protein, specifically at 20 and 40-μM concentration in PCa cells. f Effect of ZOL on inhibition of FDPS levels with ERK and AKT phosphorylation determined using Western blot in 22Rv1, C4-2B and cE2 sublines. g PCa cells were cultured in the presence of indicated doses of ZOL, and total protein lysates were analyzed for ZOL-mediated inhibition of prenylation of RhoA, Rho G, CDC-42 and H-Ras proteins. h FDPS siRNA- and scramble siRNA-transfected PCa cells were analyzed for suppression of protein prenylation using indicated antibodies.