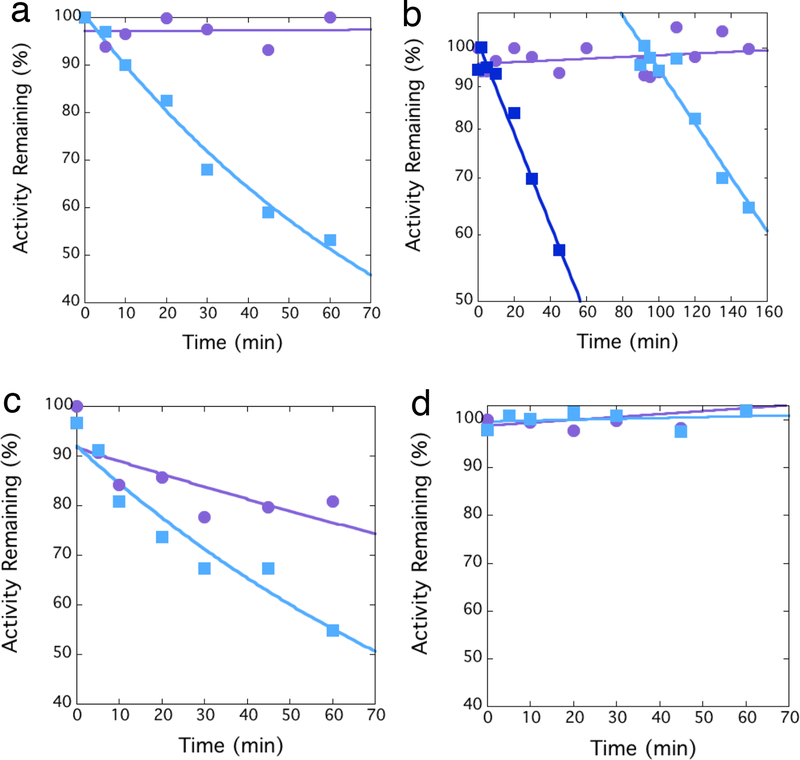
Figure 2.
Time-dependent inactivation of NDM variants. A) Dilution assays indicate time-dependent irreversible inactivation of NDM-1 by 1 ( , 10 μM), in contrast to a control incubation that omits the inactivator (
, 10 μM), in contrast to a control incubation that omits the inactivator ( ). B) Inactivation of NDM-1 by 1 (
). B) Inactivation of NDM-1 by 1 ( , 10 μM) is followed by addition of a second aliquot of fresh enzyme to the same preincubation tube (
, 10 μM) is followed by addition of a second aliquot of fresh enzyme to the same preincubation tube ( ), with the activity immediately after addition reset to 100%. A control incubation omits the inactivator (
), with the activity immediately after addition reset to 100%. A control incubation omits the inactivator ( ). C) Dilution assays indicate time-dependent irreversible inactivation of C208D NDM-1 by 1 (
). C) Dilution assays indicate time-dependent irreversible inactivation of C208D NDM-1 by 1 ( , 10 μM). The control incubation with inactivator omitted (
, 10 μM). The control incubation with inactivator omitted ( ), indicates lower stability of the C208D NDM-1 variant that wild type NDM-1. D) Dilution assays indicate no time-dependent irreversible inactivation of K211A NDM-1 by 1 (
), indicates lower stability of the C208D NDM-1 variant that wild type NDM-1. D) Dilution assays indicate no time-dependent irreversible inactivation of K211A NDM-1 by 1 ( , 10 μM), in comparison to a control incubation that omits the inactivator (
, 10 μM), in comparison to a control incubation that omits the inactivator ( ). Fitting errors from incubations that showed appreciable inactivation were <15 %.
). Fitting errors from incubations that showed appreciable inactivation were <15 %.