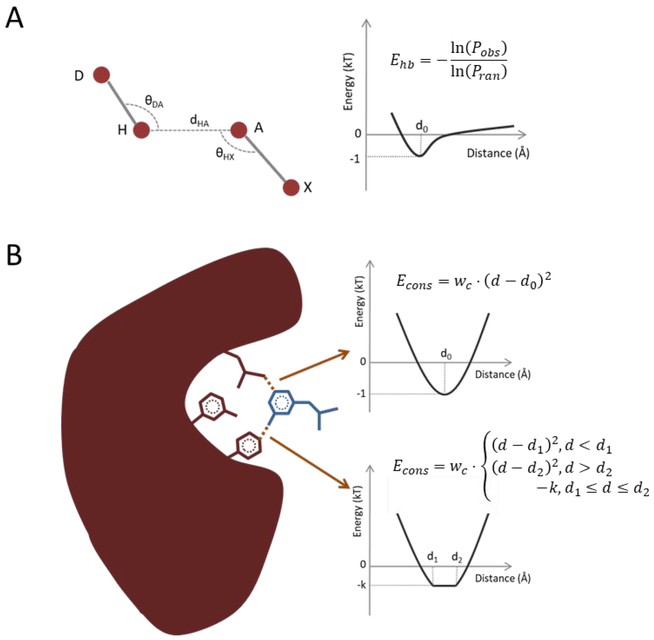
Figure 5.
(A) The hydrogen bonding energy is derived from the distribution of dHA, θDA, θHX by using the statistical energy function. Pobs is the observation frequencies; Pran is the random frequencies; D: Donor atom; H: Hydrogen atom; A: Acceptor atom; X: The heavy atom bonded with A. (B) The constraints energy is of the spring potential if a definite distance is given as the constraint, otherwise it is –k from d1 to d2 if the range is given. k is calculated by . The receptor is colored by red and the ligand is colored by blue. d1 and d2 are the lower and the upper bound of the user-provided distance range.