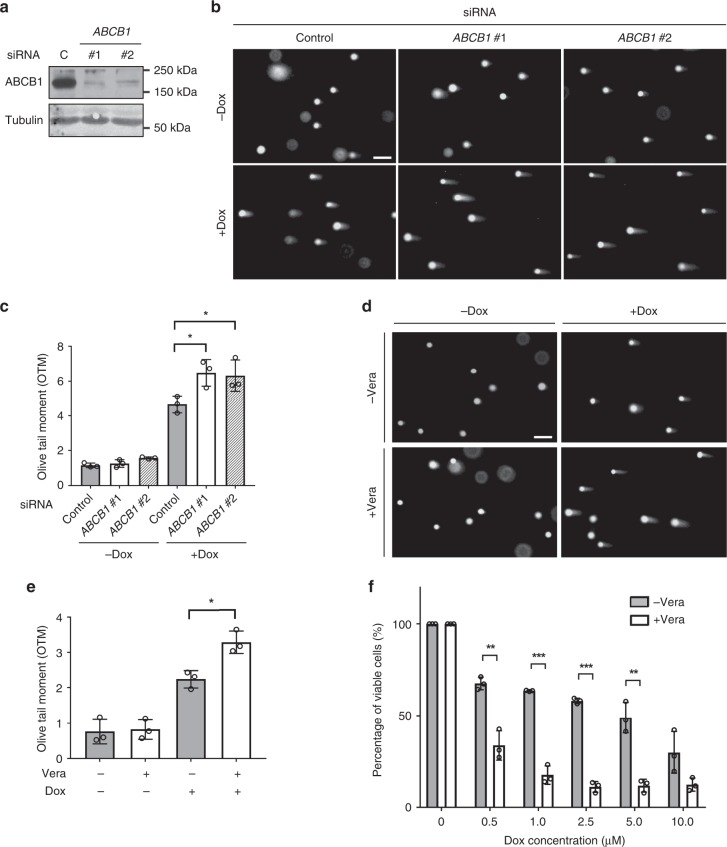
Fig. 6.
Effect of ABCB1 knockdown on doxorubicin-induced DNA damage in bat cells. a The efficiency of siRNA knockdown. PaKiT03 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNA, and the expression of ABCB1 was analysed by Western blotting. C; control siRNA. Tubulin was used as a loading control. b Comet assay of PaKiT03 cells. siRNA knockdown cells were treated without or with 10 µM doxorubicin (Dox) for 3 h, and DNA damage was visualised by comet assay. c Quantification of the amount of DNA damage calculated by olive tail moments (OTM) for the cells in (b). d Comet assay of PaKiT03 cells. Cells were pre-treated without or with 5 µM verapamil (Vera) for 30 min before the treatment with 10 µM doxorubicin alone or together with Vera for an additional 3 h. DNA damage was visualised by comet assay. e Quantification of the amount of DNA damage calculated by OTM for the cells in (d). f Quantification of cell viability. Cells were pre-treated without or with 5 µM verapamil for 30 min before the treatment with the indicated amount of doxorubicin alone or together with verapamil for an additional 3 h. Doxorubicin was then removed and replaced with the doxorubicin-free medium in the absence or presence of verapamil for 72 h before measuring cell viability. Cell viability (%) is presented relative to the control cells (the first grey bar). All data shown have at least three experimental repeats and the images are representative. Scale bar represents 50 µm. Bars represent the means ± SDs of three independent experiments. Statistical significances were calculated using unpaired student’s two-sided t test. p < 0.05 is represented with *, p < 0.01 with ** and p < 0.001 with ***