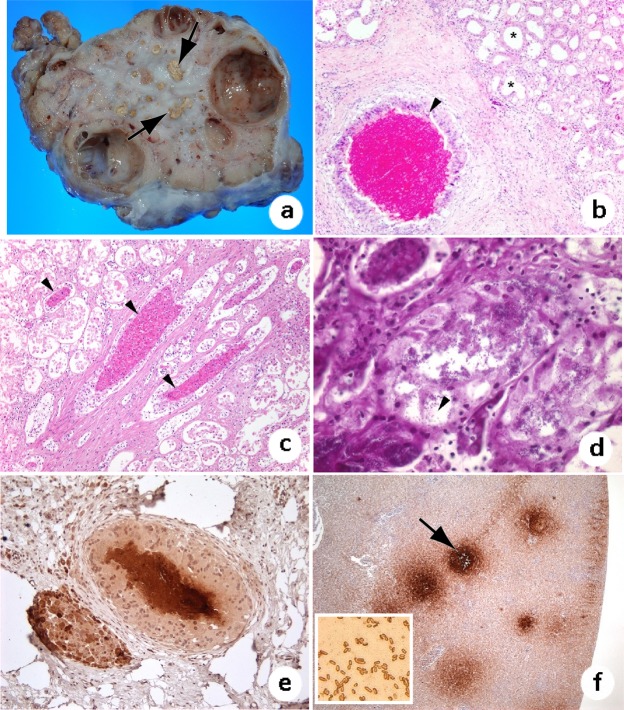
Figure 2.
Granulomatous nephritis in olive ridleys. (a) Extensive fibrosis in the kidney of stranded turtle; note variably sized caseous nodules (granulomas) on cut surface (arrow). (b) Renal granuloma (arrowhead); note core of necrotic material surrounded by macrophages, including multinucleated giant cells, and a broad zone of fibrosis. There is secondary dilation of the surrounding renal tubules (asterisks). (c) Heterophils infiltrate multiple renal tubules (arrowheads). There is detachment of the renal epithelium and other artifacts resulting from autolysis. (d) Numerous gram-negative bacilli (arrowhead) within areas of nephritis from which S. Typhimurium was isolated. (e) Immunohistochemistry staining of renal granuloma with anti-Salmonella antibodies; note brown reactivity at the center of granulomas. (f) Positive control liver from a cattle egret with multifocal necrosis from which S. Typhimurium was cultured; note S. Typhimurium-positive foci (arrow). Inset: Pure culture of S. Typhimurium bacteria staining positive with anti-S. Typhimurium antibody.