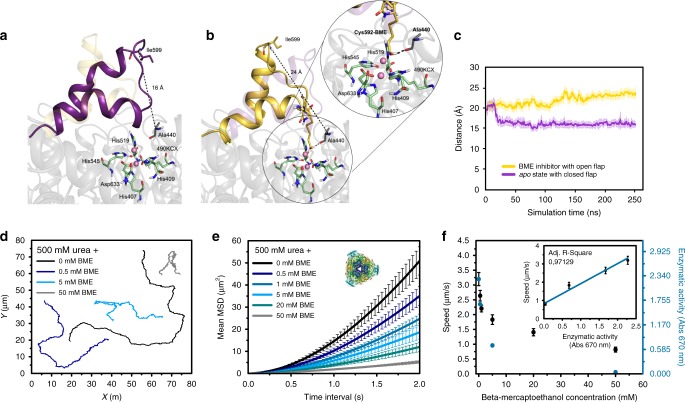
Fig. 6.
Conformation of UR and motion behavior of UR-HSMM exposed to BME. Representative snapshots taken from the MD simulations of a UR in apo state where the flap covering the active site can adopt a closed conformation (purple) and b BME which stabilizes more open conformations of the flap (yellow). The zoom of the active site residues shows catalytic residues in green, nickel atoms in pink, and the Cys592-BME inhibitor in yellow. c MD simulated flap distance between Ala440–Ile599 in the apo state (purple) and Cys592-BME state (yellow). Closed conformations have distances of about 16 Å while open conformations have 25 Å. Results are shown as the mean ± standard deviation (s.d.). d Representative trajectories of UR-HSMM exposed to 500 mM urea and different concentrations of BME. e Average MSD representation of UR-HSMM exposed to BME with urea present in excess (500 mM). Enzyme structures are extracted from RCSB PDB (see Supplementary Note 3). f Average speed of UR-HSMM, extracted from the MSD analysis and enzymatic activity for different BME concentrations with urea present in excess (500 mM). Inset: correlation of speed of UR-HSMM and its enzymatic activity depending on inhibition. Results are shown as the mean ± s.e.m. 22 Particles were analyzed for 0 and 50 mM BME, 19 particles were analyzed for 0.5 and 20 mM BME, and 21 particles were analyzed for 1 and 5 mM BME. Source data are provided as a Source Data file