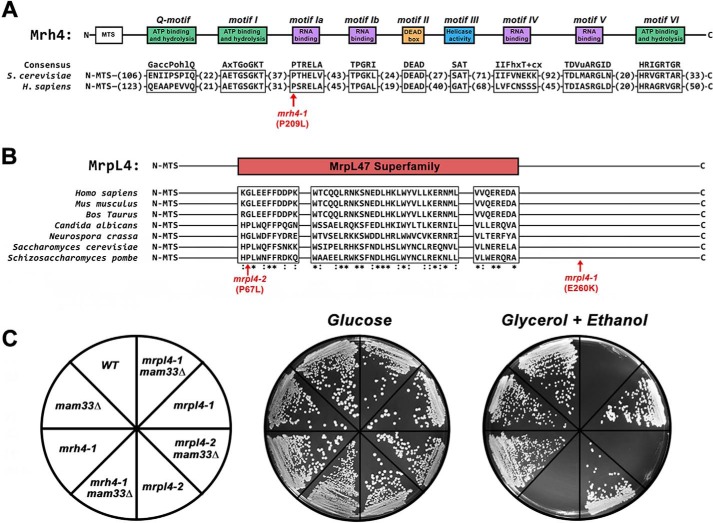
Figure 1.
Point mutations in genes necessary for mitochondrial translation are respiratory synthetic lethal with mam33Δ. A, Mrh4 and its human ortholog DDX28 contain conserved sequence motifs typical of DEAD-box RNA helicases. A single amino acid substitution in an RNA-binding domain produces a respiratory synthetic lethal phenotype in mam33Δ cells (shown in red). B, MrpL4 contains a conserved sequence domain of the MrpL47 superfamily. The two amino acid substitutions obtained from the mam33Δ respiratory synthetic lethal screen (shown in red). C, mutations in MRH4 and MRPL4 are respiratory synthetic lethal in combination with mam33Δ. Cells were streaked onto SC plates containing fermentable (glucose) or respiratory (glycerol + ethanol) carbon sources and incubated at 30 °C for 2 or 4 days, respectively.