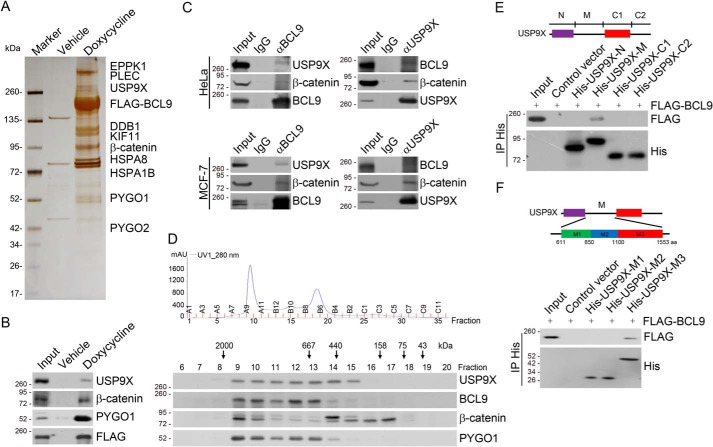
Figure 1.
BCL9 is physically associated with USP9X. A, immunoaffinity purification and MS analysis of BCL9-containing protein complexes. HeLa cells with Dox-inducible expression of stably integrated FLAG–BCL9 were collected. Cellular extracts were immunopurified with anti-FLAG–affinity beads and eluted with FLAG peptide. The eluates were resolved on SDS-PAGE and silver-stained followed by MS analysis. Detailed results from the mass spectrometric analysis are provided as shown in Table S1. B, column-bound proteins were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies against the indicated proteins. C, whole-cell lysates from HeLa or MCF-7 cells were immunoprecipitated (IP) followed by immunoblotting (IB) with antibodies against the indicated proteins. D, cellular extracts from HeLa cells were fractionated on Superose 6 size-exclusion columns. Chromatographic elution profiles (top panel) and Western blot analysis (bottom panel) of the chromatographic fractions with antibodies against the indicated proteins are shown. The elution positions of calibration proteins with known molecular masses are indicated, and an equal volume from each fraction was analyzed. E, pulldown analysis of the molecular interface involved in the interaction between BCL9 and USP9X with in vitro-transcribed/translated full-length BCL9 and His-tagged deletion mutants of USP9X purified from Sf9 cells. The conserved domains of USP9X were determined by the SMART program (Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool, http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de. Please note that the JBC is not responsible for the long-term archiving and maintenance of this site or any other third party hosted site.). The purple rectangle represents α-α super-helix in the N-terminal region of USP9X (amino acids 249–610), and the red rectangle represents the peptidase C19 domain in the C-terminal region of USP9X (amino acids 1,554–1,953). F, pulldown analysis of the molecular interface involved in the interaction between BCL9 and USP9X with in vitro-transcribed/translated full-length BCL9 and His-tagged deletion mutants M1, M2, or M3 of USP9X purified from Sf9 cells.