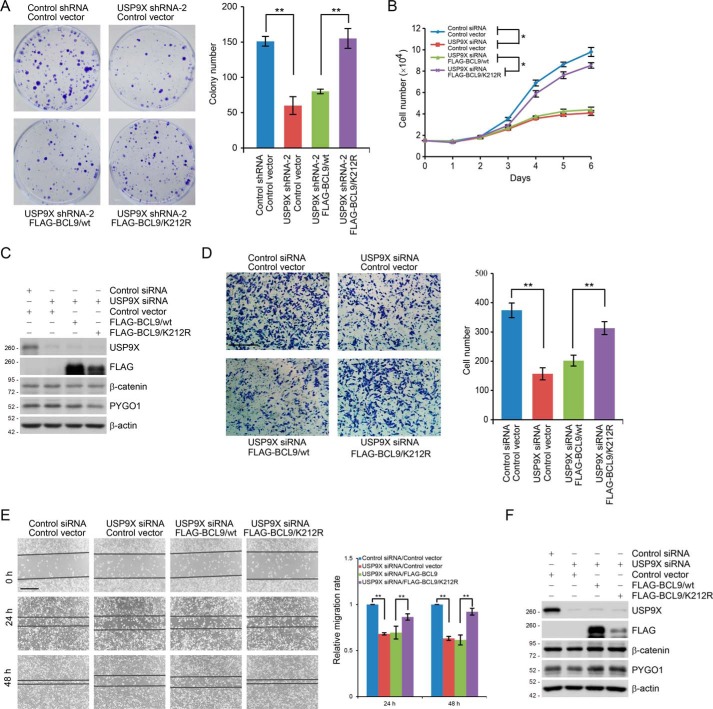
Figure 6.
USP9X promotes breast cancer cell proliferation and invasion through targeting BCL9. A, colony formation assays with MCF-7 cells stably expressing control shRNA or USP9X shRNA and FLAG–BCL9/WT or FLAG–BCL9/K212R. Representative images from three biological experiments are shown. Each bar represents the mean ± S.D. for three biological experiments. **, p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA. B, MCF-7 cells stably expressing FLAG–BCL9/WT or FLAG–BCL9/K212R were transfected with control siRNA or USP9X siRNA and then subjected to growth viability assay. Each bar represents the mean ± S.D. for three biological experiments. *, p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA. C, cellular extracts from cells used in B were collected and analyzed by Western blotting. D, MDA–MB-231 cells stably expressing FLAG–BCL9/WT or FLAG–BCL9/K212R were transfected with control siRNA or USP9X siRNA followed by transwell invasion assays. Each bar represents the mean ± S.D. for three biological experiments. **, p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA. Scale bar, 50 μm. E, MDA–MB-231 cells stably expressing FLAG–BCL9 or FLAG–BCL9/K212R were transfected with control siRNA or USP9X siRNA and then subjected to wound healing scratch assays. Each bar represents the mean ± S.D. for three biological experiments. **, p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA. Scale bar, 50 μm. F, cellular extracts from cells used in D and E were collected and analyzed by Western blotting.