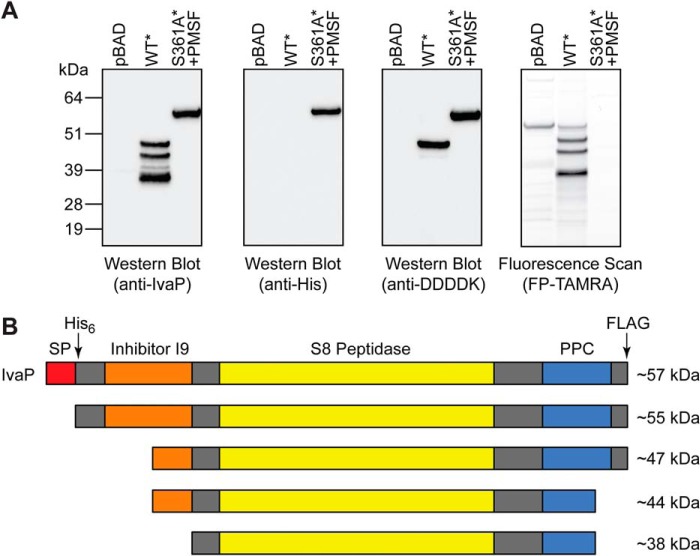
Figure 2.
IvaP maturation requires sequential N- and C-terminal processing. A, Western blotting (left) and in-gel fluorescence (right) analysis of FP-TAMRA-labeled supernatants from stationary-phase cultures of ΔivaP V. cholerae C6706 expressing empty vector (pBAD), IvaP* (WT*), or IvaPS361A* (S361A*). Cultures were supplemented with PMSF (S361A*) or vehicle control (pBAD, IvaP*) as described under “Experimental procedures.” These analyses were repeated three times with consistent results. B, proposed model of the major cleavage events that accompany IvaP maturation. Approximate molecular masses corresponding to native IvaP precursors detected in stationary-phase cultures are shown. The predicted protein domain structure of IvaP was determined using the Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool (version 8.0) (41). SP, signal peptide. PPC, bacterial prepeptidase PPC domain. The arrows indicate positions of His6 and FLAG tags in IvaP* and IvaPS361A*.