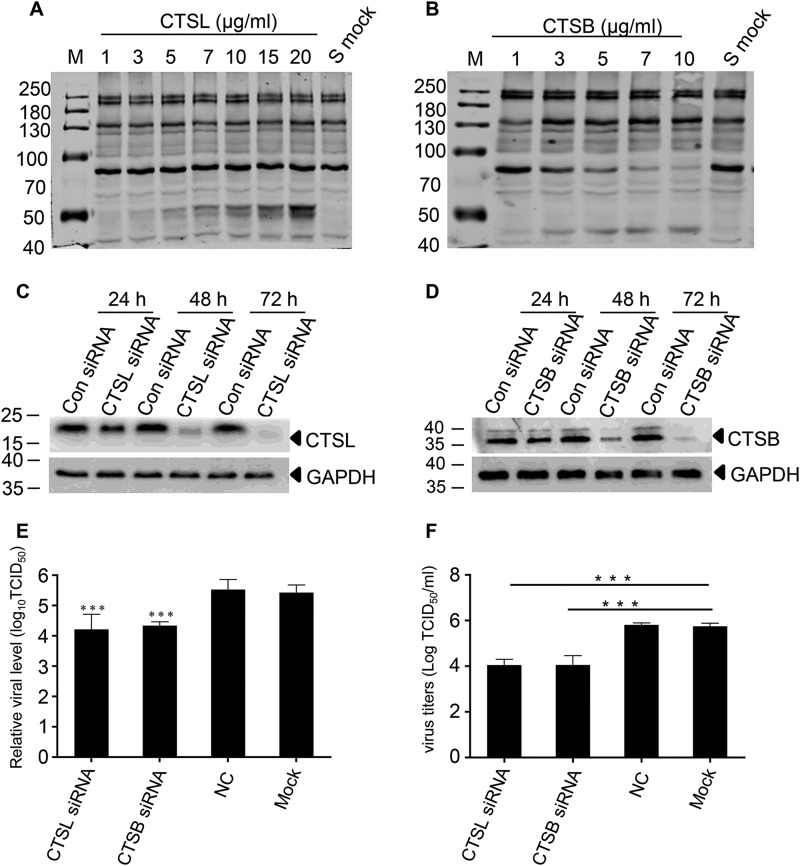
Figure 2.
PDCoV entry is activated by CTSL and CTSB. A and B, CTSL (A) and CTSB (B) cleaved S protein. The S protein was expressed in 293T cells and the enzyme cleavage assay was performed with recombinant cathepsin L and cathepsin B in Dulbecco's phosphate-buffered saline (pH 5.6), respectively. C and D, the expression of CTSL (C) or CTSB (D) was significantly inhibited by gene-specific siRNA. CTSL- and CTSB-specific siRNA were designed and transfected into IPI-2I cells to knock down endogenous CTSL or CTSB expression. The protein expression at different times was detected by Western blotting. E, siRNA for CTSL or CTSB dramatically decreased virus entry. IPI-2I cells were transfected with siRNAs of CTSL or CTSB; 48 h later, the cells were infected with PDCoV (m.o.i. = 1), then NS7a sgRNA was detected with real-time PCR at 6 h post-infection. F, siRNA for CTSL or CTSB dramatically decreased the virus yield. Following transfection with siRNAs, IPI-2I cells were infected with PDCoV (m.o.i. = 0.01). The viral dose was measured by calculating TCID50 at 48 h post-infection. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.D. for triplicate samples. Level of significance was determined by Student's t test. ns, p > 0.05; ***, p < 0.001.