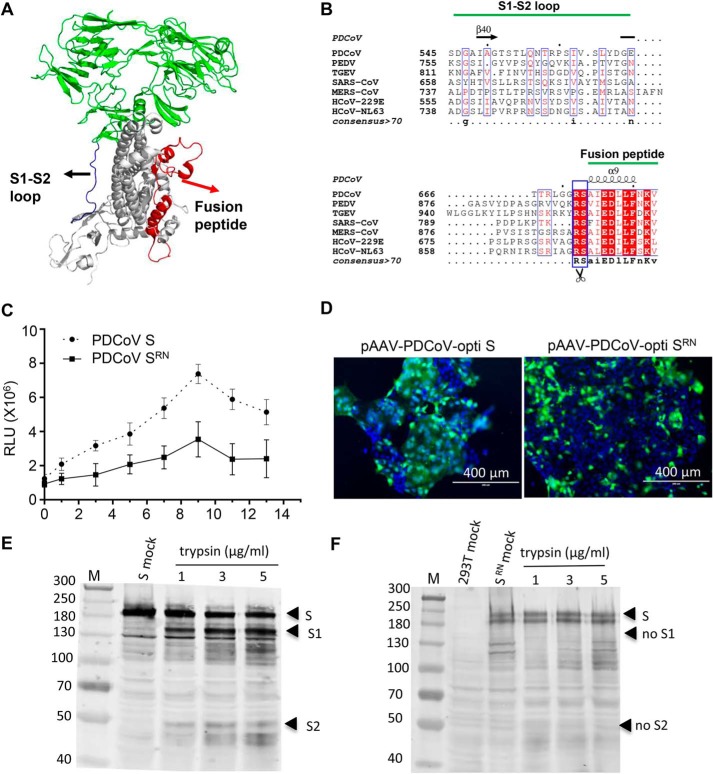
Figure 6.
Arg-672 in the S protein is crucial for trypsin-induced cell to cell fusion. A, the monomer structure of the PDCoV spike protein was determined by cryo-EM (PDB ID: 6B7N). Loop regions between S1 and S2 domains and fusion peptide are indicated with blue and red, respectively. B, sequence conservation among the coronavirus glycoproteins. Multiple sequence alignment of the coronavirus S protein sequences. PDCoV strain NH (GenBankTM: ANA78450.1), PEDV CV777 (GenBankTM: AAK38656.1), TGEV Purder strain (GenBankTM: ABG89335.1), SARS coronavirus Urbani (GenBankTM: AAP13441.1), MERS-CoV (GenBankTM: AVN89453.1), HcoV-229E (GenBankTM: ARB07392.1), and HcoV-NL63 (GenBankTM: AFV53148.1). The secondary structure of the PDCoV S protein is indicated above the sequence. C, the R672N mutant inhibited trypsin-induced cell fusion. Effector cells (293T) were co-transfected with WT (pCAGGS-opti S) or mutant S-expressing plasmid (pCAGGS-PDCoV opti-SRN) and pCDNA3.1-T7 vectors. The target cells (ST) were transfected with the pET-32a-IRES-luc plasmid, and then the ST cells were quickly trypsinized and overlaid with 293T cells followed by various concentrations of trypsin treatment to induce cell fusion. Luciferase activity was measured using a luciferase assay kit (Promega) with an EnSpire® multifunctional microplate reader (PerkinElmer). D, cell fusion was significantly inhibited by the R672N mutant. ST cells were transfected with pAAV-PDCoV-opti S and pAAV-PDCoV opti-SRN; 48 h post-transfection, the cells were treated with 100 μg/ml trypsin in DMEM for 10 min at room temperature and cell fusion was detected with a fluorescence microscope. The introduction of a furin site at Arg-672 induced PDCoV S-mediated cell fusion. E and F, 293T cells were transfected with pAAV-PDCoV-opti S (E) and pAAV-PDCoV opti-SRN (F) plasmid. At 48 h post-transfection, cells were collected to perform trypsin cleavage assay.