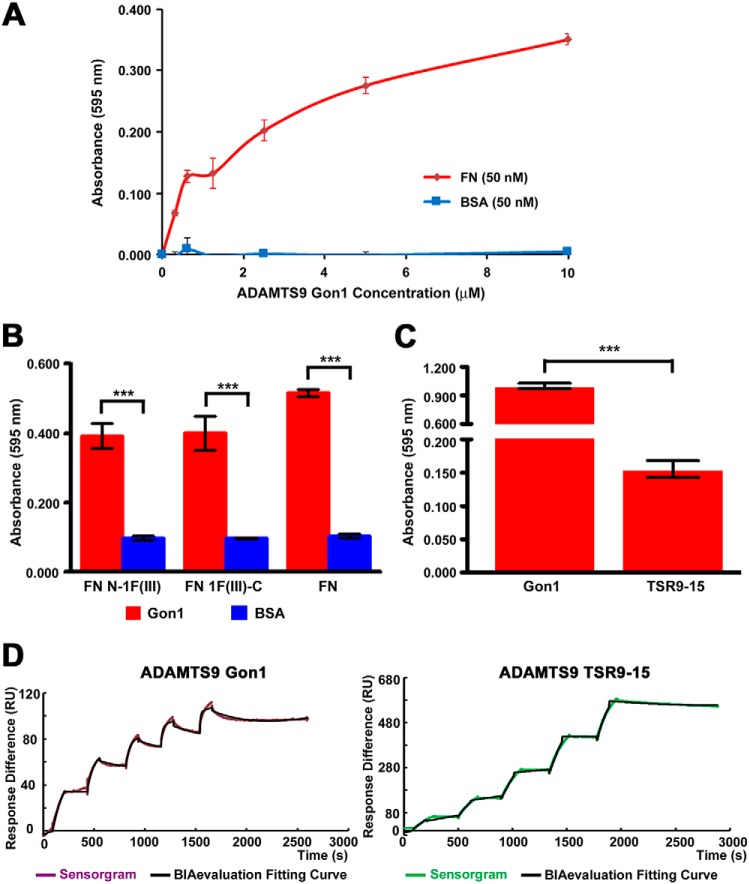
Figure 2.
Fibronectin binding to ADAMTS9 constructs. A, solid-phase binding assay of ADAMTS9 Gon1 module to immobilized fibronectin (FN, red line). BSA (blue line) was used as a control for binding. B, ADAMTS9 Gon1 module was tested for binding to N- and C-terminally truncated fibronectin constructs N-1F(III) and 1F(III)-C, respectively. Binding to these constructs was compared with binding to BSA (negative control). ***, p < 0.0001, n = 4. C, solid-phase binding assay comparing ADAMTS9 Gon1 and ADAMTS9 TSR9–15 binding to fibronectin. ***, p < 0.0001, n = 4. D, surface plasmon resonance analysis of plasma fibronectin (analyte, 16.9–270 mm) binding to ADAMTS9 Gon1 module immobilized on a CM5 chip. The binding KD was 2.8 nm, χ2/Rmax = 4% for ADAMTS9 Gon1, and 104 nm (χ2/Rmax = 6%) for ADAMTS9 TSR9–15. The purple and green lines represent the sensorgram, and the black line is the fitted curve produced by BIAevaluation software.