Figure 10.
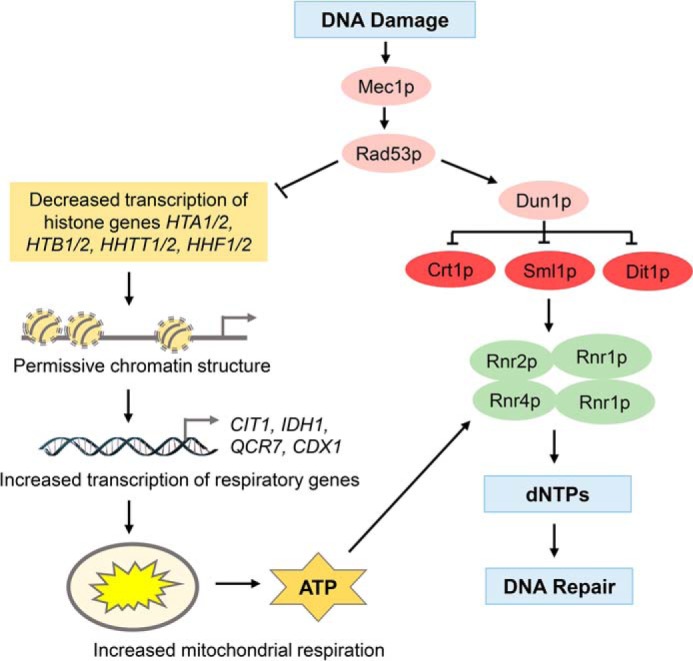
Model depicting DDR-induced respiration. DDR, in a Mec1p- and Rad53p-dependent way, regulates dNTP synthesis by a bifurcating mechanism. In one well-established branch of the pathway, Dun1p inactivates Crt1p, Sml1p, and Dif1p, leading to increased RNR activity and dNTP synthesis. In the second branch of the pathway, Mec1p and Rad53p down-regulate transcription of histone genes. Decreased histone levels result in altered chromatin structure and induction of TCA cycle and ETC genes required for respiration. A direct outcome of elevated respiration is increased production of ATP, a potent allosteric activator for the RNR enzyme, increased synthesis of dNTPs, and improved cell survival.
