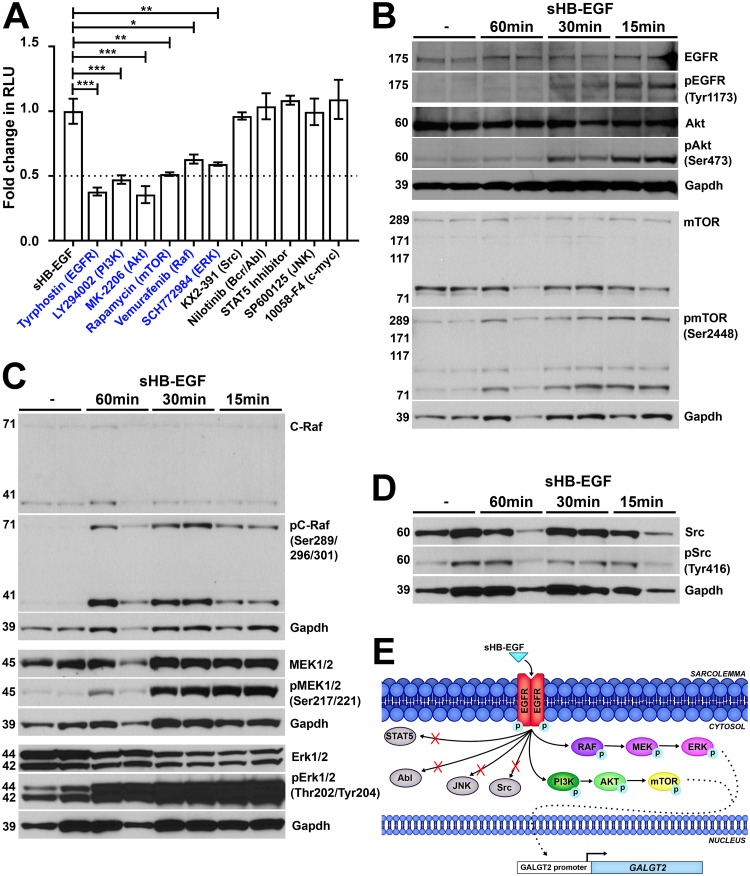
FIG 4.
sHB-EGF stimulates phosphorylation signaling cascades in skeletal muscle cells. (A) sHB-EGF was added to C2C12 myotube cultures in the presence of drugs that block specific signal transduction pathways. Drugs in blue showed significant decreases in sHB-EGF activation of the GALGT2 promoter relative to sHB-EGF alone. GALGT2 promoter luciferase reporter activity was measured in relative light units (RLU). Errors are SEM for n = 12 measures per condition. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Fold changes are reported relative to the level of sHB-EGF alone, set to 1. (B to D) Western blots of C2C12 myotube protein lysates before or after sHB-EGF addition for 15, 30, or 60 min using antibodies to GAPDH protein (a protein loading and transfer control). Western blots in panel B were additionally probed for members of the Akt signaling pathway, including antibodies to EGFR, Akt, and mTOR protein or antibodies specific to phosphorylated EGFR (at Tyr1173), Akt (at Ser473), and mTOR (at Ser2448). Western blots in panel C were probed for members of the RAF signaling pathway, including antibodies to C-Raf, MEK1/2, and Erk1/2 protein or antibodies specific to phosphorylated C-Raf (at Ser289/296/301), MEK1/2 (at Ser217/221), and Erk1/2 (at Thr202/Tyr204). Western blots in panel D were probed for Src protein or phosphorylated Src (at Tyr416). (E) Diagram illustrating the pathways utilized by sHB-EGF to activate the GALGT2 promoter in skeletal muscle.