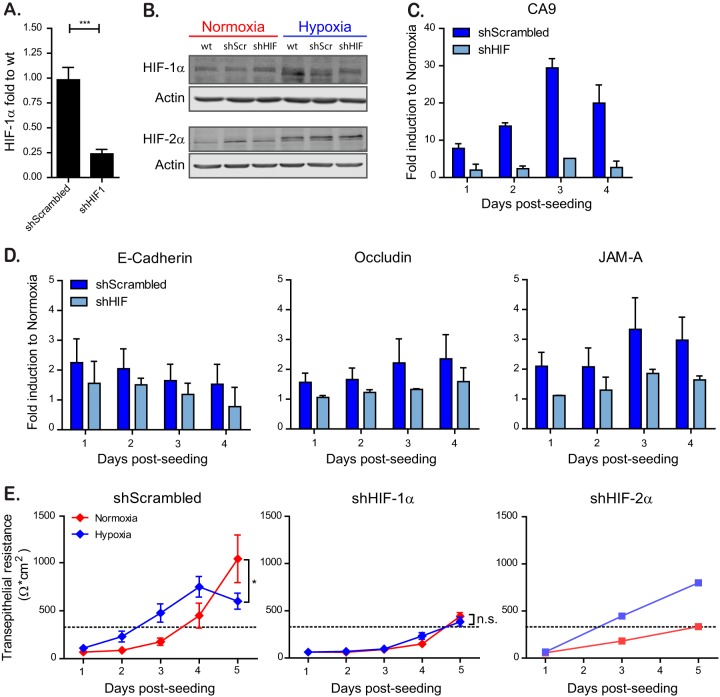
FIG 3.
HIF-1α is responsible for faster barrier establishment under hypoxic conditions. T84 cells were transduced with lentiviruses expressing an shRNA targeting HIF-1α or a scrambled control. (A) Knockdown of HIF-1α was controlled by qPCR. (B) T84 cells knocked down for HIF-1α or expressing a scrambled control were incubated under normoxic or hypoxic conditions. At 6 h postincubation, protein samples were harvested and evaluated by Western blotting for HIF-1α or HIF-2α. Each experiment was performed in triplicate; a representative image is shown. (C) T84 cells expressing a scramble shRNA or a shRNA against HIF-1α were evaluated for their induction of the hypoxic marker CA9 over the indicated time course by qPCR. The results are normalized to normoxic values for each day. (D) T84 cells expressing a scramble shRNA or a shRNA against HIF-1α were evaluated for their induction of tight junction proteins over the indicated time course by qPCR. The results are normalized to normoxic values for each day. (E) T84 cells expressing a scramble shRNA or a shRNA against HIF-1α or HIF-2α were seeded on Transwell inserts. Cells were incubated in normoxic or hypoxic conditions, and TEER measurements were taken at 24-h intervals for 5 days. A TEER of >330 Ω ⋅ cm2 indicates complete barrier formation and is marked by a dotted line. Values shown represent means ± the SEM (n = 9) from triplicate experiments for shScrambled and shHIF-1α. For shHIF-2α, one representative experiment is shown of two different anti-HIF-2α shRNAs tested. *, P < 0.05; n.s., not significant (two-way ANOVA). (A, C, and D) Values shown represent the means plus the SD from three independent experiments (***, P < 0.001; one-sample t test on log-transformed fold changes).