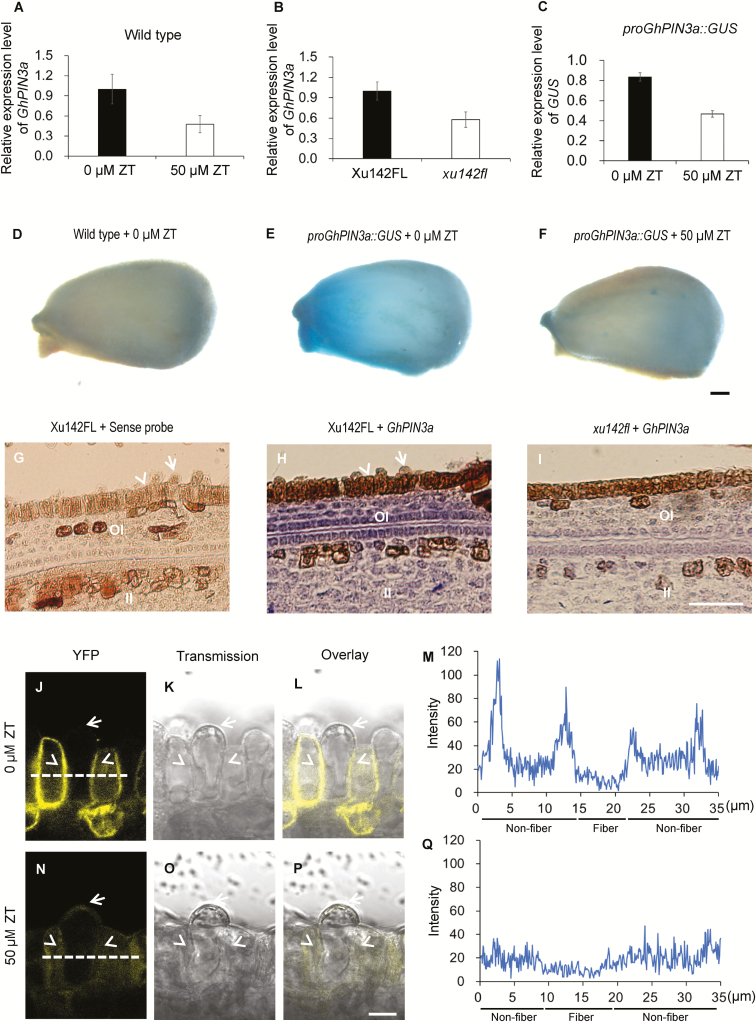
Fig. 6.
Cytokinins inhibit auxin accumulation in the ovule epidermis of cotton through disturbing GhPIN3a-mediated polar auxin transport. (A) GhPIN3a transcription levels in ZT-treated ovules and the control. Wild-type ovules at 0 d post anthesis (DPA) were treated with 50 μM ZT for 12 h, and then used for RT-qPCR assays. (B) GhPIN3a transcription levels in the outer integument of ovules of the fiberless xu142fl mutant and the Xu142FL wild-type at 0 DPA. (C) GUS transcription levels in ZT-treated proGhPIN3a::GUS ovules and the control. proGhPIN3a::GUS ovules at 0 DPA were treated with 50 μM ZT for 12 h and then used for RT-qPCR assays. Transcription levels (in arbitrary units) are normalized to that of GhHIS3. Data are means (±SD) of three repeats. (D–F) GUS staining of ovules of the wild-type control (D), proGhPIN3a::GUS (E), and ZT-treated proGhPIN3a::GUS (F). Ovules at 0 DPA were treated with or without 50 μM ZT for 12 h. The scale bar is 250 μm. (G–I) GhPIN3a RNA in situ hybridization in the integument of ovules of xu142fl (I) and Xu142FL (H). Transcription of GhPIN3a was repressed in xu142fl as compared with that in Xu142FL. Sections (10 μm) from ovules at 0 DPA were used for in situ hybridization with the GhPIN3a antisense probe. The sense probe was used as the negative control (G). OI, outer integument; II, inner integument. The scale bar is 20 μm. (J–Q) GhPIN3a::YFP localization in the ovule epidermal layer. The polar localization of GhPIN3a::YFP in non-fiber cells was impaired in ovules treated with ZT (N, P, Q) as compared with the control (J, L, M). Ovules at 0 DPA were sectioned by hand and then immersed in 50 μM ZT. After 30 min incubation in the dark, the samples were washed with distilled water and then mounted for observation. Fluorescence intensity along the dashed lines in (J) and (N) was shown in (M) and (Q), respectively. The scale bars is 10 μm. Arrows indicate fiber cells, and arrowheads indicate non-fiber cells in the ovule epidermis.