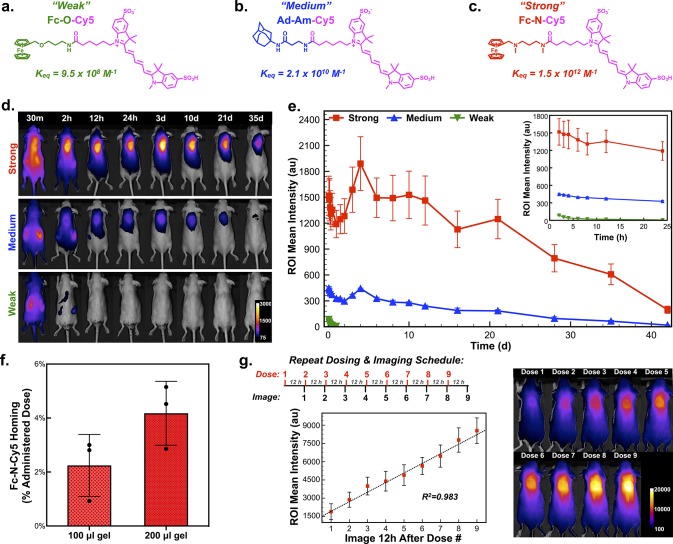
Figure 3.
Determination of host–guest affinity required for complex formation in the body after systemic administration. (a) Structure of model prodrug from a ferrocene guest conjugated to a near-infrared cyanine dye (Cy5), termed the “Weak” guest (Fc-O-Cy5), with a measured affinity for CB[7] of 9.5 × 108 M–1. (b) Structure of model prodrug from an adamantyl guest conjugated to Cy5, termed the “Medium” guest (Ad-Am-Cy5), with a measured affinity for CB[7] of 2.1 × 1010 M–1. (c) Structure of model prodrug from a ferrocene guest conjugated to Cy5, termed the “Strong” guest (Fc-N-Cy5), with a measured affinity for CB[7] of 1.5 × 1012 M–1. (d) F127-CB[7]:PEG8-Fc hydrogels injected subcutaneously, with subsequent administration of the three model dye-linked guests and representative in vivo fluorescence imaging to quantify dye homing to the site of the hydrogel. (e) Quantification of the average intensity in the hydrogel region of interest over time following administration of the three model dye-linked guests (n = 4). (f) Results from dye quantification following explantation of 100 μL and 200 μL hydrogels, dye extraction, and quantification. (g) Studies evaluating repeat loading of subcutaneous hydrogels with nine consecutive doses of Fc-N-Cy5 administered with 12-h spacing and imaging conducted immediately prior to administration of the next dose, as displayed in the study timeline. The average signal intensity arising from the dye at the hydrogel site was quantified and plotted (n = 4).