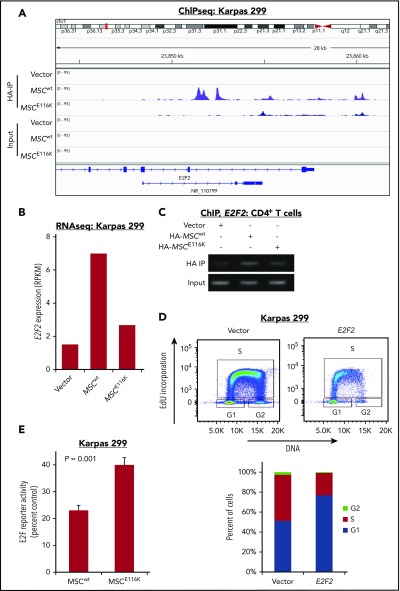
Figure 4.
E2F2 is a transcriptional target of MSCwt that inhibits the cell cycle in ALCL cells. (A) ChIP-seq in Karpas 299 cells showed binding of MSCwt, but not MSCE116K, to several sites upstream and downstream of the E2F2 transcriptional start site. NR_110799 represents an uncharacterized noncoding RNA gene, LOC101928163, which was not expressed at the RNA level in any of the samples. The data shown are from the same ChIP-seq experiment as the motif analysis shown in Figure 2E. (B) Corresponding RNAseq data showed a 4.7-fold induction of E2F2 expression in Karpas 299 cells transduced with MSCwt compared with vector-only control that was largely reversed by MSCE116K. Representative results from 2 independent experiments. (C) ChIP in normal T cells confirmed MSCwt binding to E2F2. (D) Overexpression of E2F2 in Karpas 299 cells, which have low basal levels of MSC and E2F2, inhibited cell cycle progression via G1 arrest. (E) MSCE116K increased E2F reporter activity in luciferase assays, consistent with its ability to block expression of repressive E2F2. Data reflect 3 independent experiments and are shown as mean ± SD. The Student t test was used to compare results. RPKM, reads per kilobase of transcript per million mapped reads.