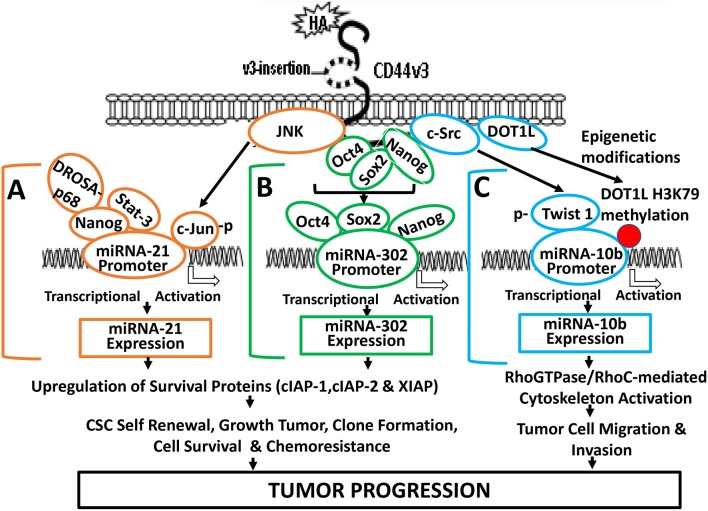
Figure 3.
A proposed model for HA-CD44-mediated signaling activation in the regulation of miRNA-21, miR-302, and miR-10b production and oncogenesis in tumor cells. (A) The binding of HA to CD44 promotes JNK activity which, in turn, causes phosphorylation of c-Jun. Phosphorylated c-Jun then binds to the miR-21 promoter and induces miR-21 expression. HA binding to CD44 also causes Nanog interaction with Stat-3 and the microprocessor complex containing the RNase III (DROSHA) and the RNA helicase (p68). These Nanog-associated signaling complexes (containing Stat-3 and/or DROSHA and p68) then bind to miR-21 promoter region, resulting in miR-21 production leading to upregulation of IAP protein expression, tumor cell survival, and chemoresistance. (B) HA-CD44 interaction promotes miRNA-302 expression and chemoresistance: HA binding to CD44 promotes an association between CD44v3 and OCT4/SOX2/Nanog. Subsequently, OCT4/SOX2/Nanog complexes interact with the promoter region (containing OCT4-, SOX2-, and Nanog-binding sites) of the miR-302 cluster resulting in miR-302 cluster gene expression and mature miR-302 production. The resultant miR-302 then functions to induce IAP (cIAP-1, cIAP-2, and XIAP) expression, tumor cell growth, self-renewal, clone formation, tumor cell survival, and chemoresistance in tumor cells. (C) HA-CD44 interaction promotes miRNA-10b expression and tumor migration/invasion: HA binding to CD44 promotes c-Src phosphorylation (kinase activation), which, in turn, causes phosphorylation of Twist. Phosphorylated Twist then interacts with the E-box elements of mR-10b promoter, resulting in miR-10b gene expression, and mature miR-10b production. The binding of HA to CD44 also enhances DOT1L upregulation and DOT1L/H3K79 methylation-mediated epigenetic changes, resulting in methyl-H3K79 binding to miR-10b promoter, and miR-10b gene expression/production. The expressed miR-10b then promotes upregulation of RhoGTPase-mediated cytoskeleton activation leading to tumor cell migration and invasion. Red dot represents DOT1L/H3K79-mediated histone modifications (via epigenetic changes).