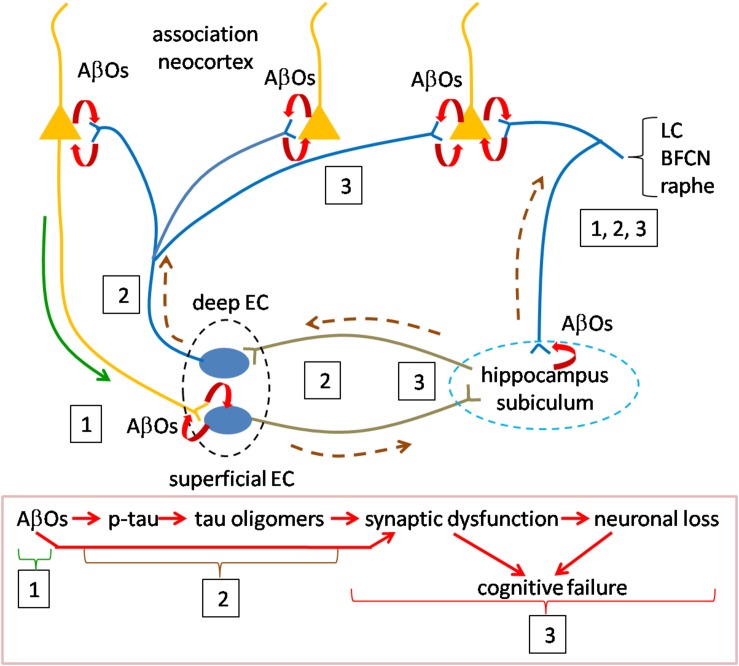
FIGURE 2.
Speculative scheme to explain AD pathogenesis. Overview of pathogenesis is summarized in the red boxed caption at the bottom. Initiating pathogenesis: The process would be initiated by the formation of AβOs in cortical neurons. The source of AβOs would include those produced locally within the presynaptic terminals of cortical neurons innervating entorhinal cortex. AβOs produced in the somatodendritic domain of cortical neurons could serve as the nidus for local amyloid plaque deposition and would be in contact with axons of entorhinal cortical neurons. Thus, AβOs produced in both the cortico-entorhinal and entorhinal-cortical projections may participate in formation of AβOs, The initial focus of AβO actions (signified by boxed number 1) may be registered in superficial entorhinal cortex whose neurons receive cortical inputs. At later stages retrograde AβOs acting on entorhinal axons in cortex may contribute to pathogenesis, as may AβOs produced in entorhinal afferents to cortex (boxed 3). Driving pathogenesis: AβO acting on entorhinal neurons would catalyze formation of tau oligomers with subsequent spread and propagation in connected neurons, first in hippocampus and subiculum and then association neocortex (boxed 2). Toxic tau oligomers could exert injury to the neurons in which they are formed and following release to the synapses and neurons to which they spread and in which they propagate (boxed 3). AβOs could interact during this phase with tau oligomers to enhance synaptic and neuronal dysfunction. Neurons in the locus coeruleus, basal forebrain cholinergic complex and raphe nuclei may owe their selective vulnerability to their connections with both neocortex and hippocampus during early and later phases (boxed 1, 2, 3). Curved red arrows signify local production of AOs due to processing of APP. Green solid line (near boxed 1) indicates the anterograde transport of APP for processing at the presynapse during the initial phase; AβOs produced in somatodendritic domains could also be transported anterogradely at this stage (green line). Brown dashed line represents the direction of tau oligomer spread. LC, locus coeruleus neuron; BFCN, basal forebrain cholinergic neuron; and EC, entorhinal cortex neuron.