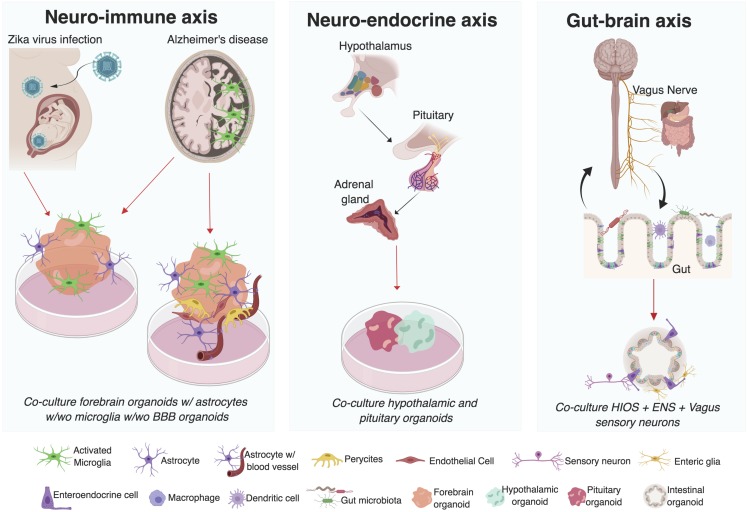
FIGURE 1.
Investigating interactions between multiple systems using organoid co-culture systems. Mechanisms underlying the neuro-immune, neuro-endocrine, and gut-brain axis in humans can be investigated utilizing organoid co-culture systems. Advances have already been made in the use of brain region specific organoids co-cultured with microglia (resident immune cells in the brain) in the study of ZIKV induced microcephaly and Alzheimer’s disease. Similarly, advances in the development of blood brain barrier (BBB) stem cell models highlights the exciting possibility of investigating the role of the BBB thinning in AD pathogenesis. Enteric organoids that combine intestinal (HIOs) and enteric nervous system (ENS) cellular components and vagal sensory neurons suggest the possibility to interrogate the mechanisms underlying the gut-brain interactions in vitro. Finally, the development of different organoid models of human pituitary and hypothalamic tissue has also been reported. Even though to date there is no organoid model of the adrenal gland, this could potentially be used to interrogate different components of the neuro-endocrine axis. (Figure was created with BioRender.com softwared. Abbreviations used w/wo is with or without).