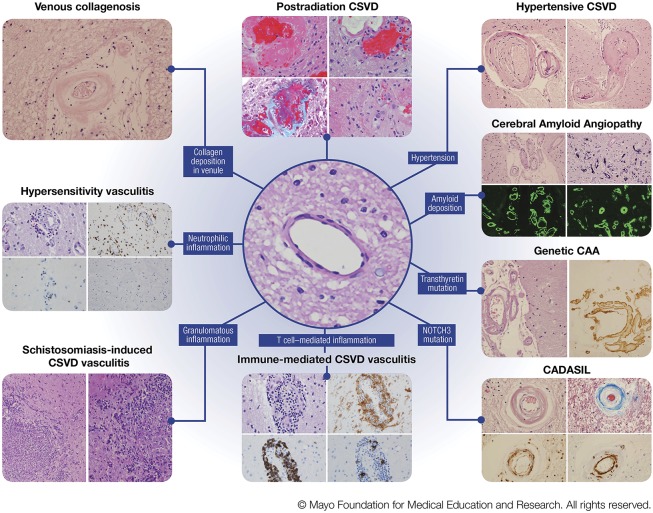
Figure 2. Various pathologic characteristics of CNS small vessel disease.
Left column, venous collagenosis. H&E stain of a periventricular venule in the white matter with thickened walls and collagen deposition. Hypersensitivity vasculitis. (Top left) H&E stain showing features of leukoctyoclastic vasculitis; (top right) CD68 immunohistochemistry for macrophages; (bottom left) CD20 showing sparse B lymphocytes; (bottom right) CD3 showing rare T lymphocytes. Schistosomiasis-induced CSVD vasculitis. (Left and right) H&E stains showing granulomatous inflammation. Middle column, postradiation CSVD. (Top left) H&E stain showing fibrinoid necrosis; (top right) H&E stain showing capillary ectasia and atypical nuclear changes; (bottom left) trichrome stain showing collagenosis (blue) and fibrinoid material; (bottom right) H&E stain showing obliterative collagenosis of small vessels with nuclear atypia. Center image, H&E stain showing a normal subcortical white matter arteriole. Immune-mediated CSVD vasculitis. (Top left) H&E stain showing cellular infiltrates in vessel wall; (top right) HLA-DR immunohistochemistry showing macrophage infiltrates; (bottom left) CD20 immunohistochemistry showing B-lymphocytic infiltrates; (bottom right) CD3 showing T-lymphocytic infiltrates. Right column, hypertensive CSVD. (Left) H&E stain showing hyaline arteriolar sclerosis; (right) H&E stain showing a microaneurysm. Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy. (Top left) H&E stain showing amyloid-β-laden vessels in the subarachnoid spacewith the doublebarreled appearance; (top right) capillaries with calcium mineralization; (bottom left) leptomeningeal CAA on thioflavin S fluorescent microscopy; (bottom right) parenchymal CAA on thioflavin S fluorescent microscopy. Genetic CAA/novel transthyretin mutation. (Left) H&E stain showing leptomeningeal arteriole involvement; (right) transthyretin immunohistochemistry. CADASIL. (Top left) H&E stain showing loss of smooth muscle cells; (top right) trichrome stain showing collagen deposition (blue) in wall of affected arteriole; (bottom left) ubiquitin immunohistochemistry showing granular deposits in arterial wall; (bottom right) smooth muscle actin immunohistochemistry showing fragmentation and loss of smooth muscle cells in affected arteriole. Abbreviations: CAA = cerebral amyloid angiopathy; CADASIL = cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy; CSVD = central nervous systemsmall vessel disease. H&E = hematoxylin-eosin (Figure used with permission of Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research).