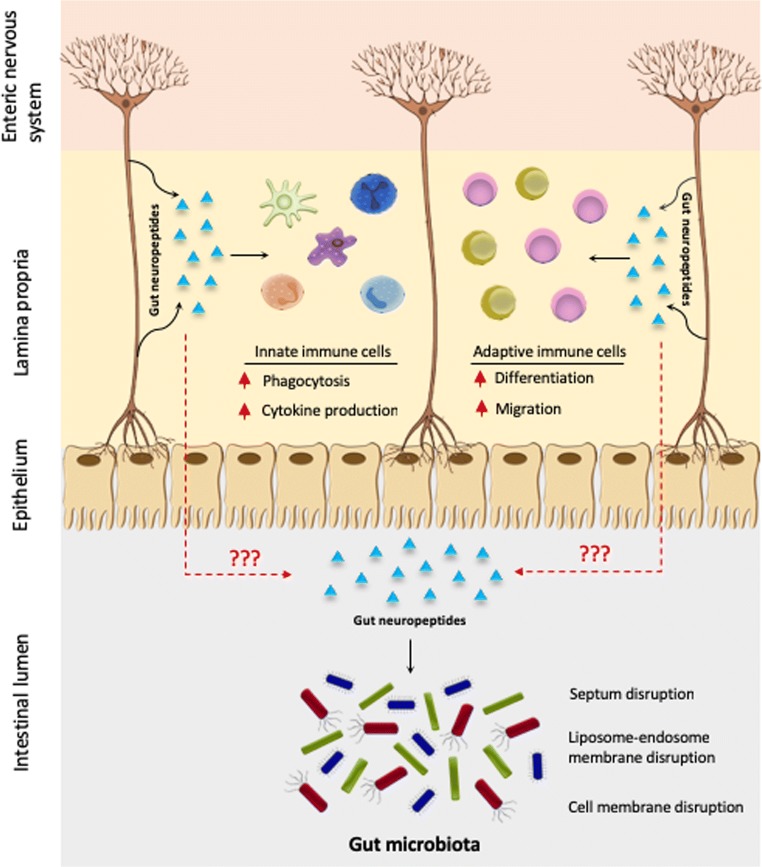
Fig. 1.
Direct and indirect effects of gut neuropeptides in the GIT. Upon sensing of stressful stimuli, enteric neurons release gut neuropeptides that induce a response in innate and adaptive immune cells, which also secrete these peptides, resulting in a strong response to bacterial imbalance. Additionally, if gut neuropeptides cross the epithelial barrier, they could exert a direct antimicrobial activity in the intestinal lumen by different killing mechanisms