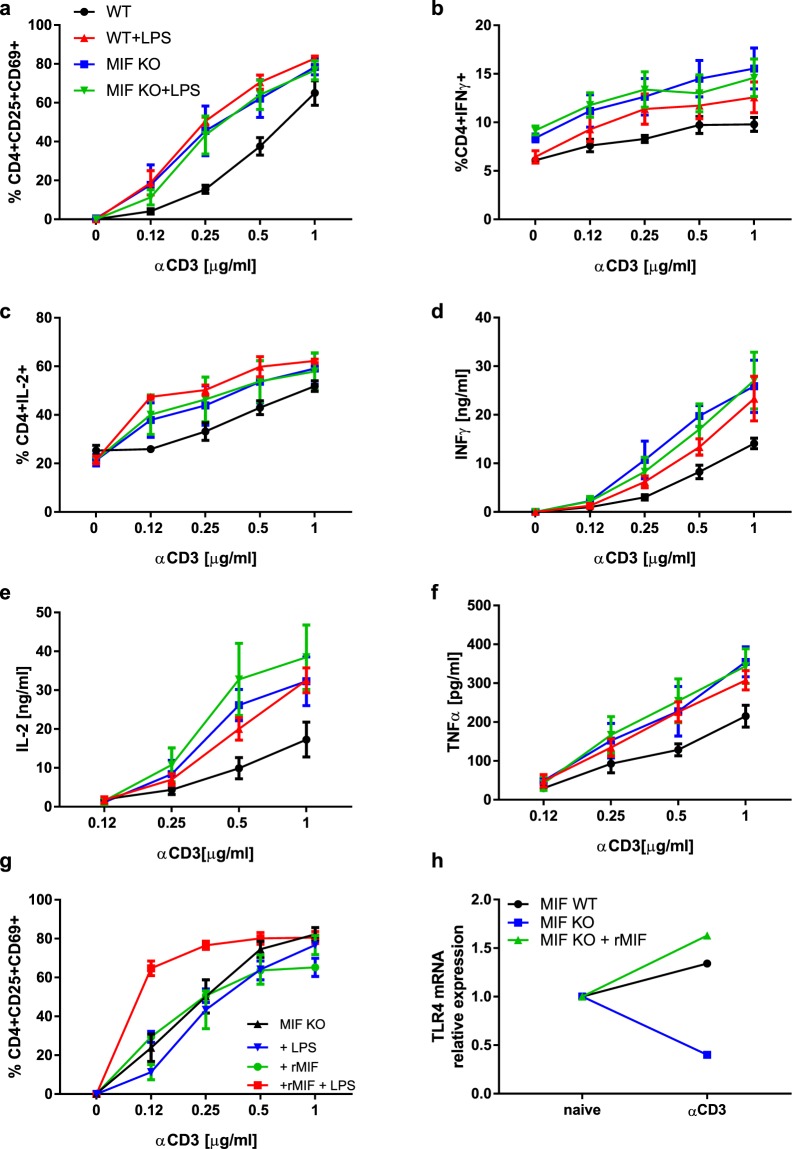
Figure 5.
MIF mediates LPS-induced activation of CD4+ T lymphocytes by modulating the expression of TLR4 (a) Activation of WT and MIF-deficient CD4+ T cells in presence of LPS. Data are means ± SEM from three experiments. (b) Percentages of IFNγ-producing CD4+ T cells induced by LPS. Data are means ± SEM from four experiments. (c) Percentages of IL-2-producing CD4+ T cells. Data are means ± SEM from three experiments. (d) IFNγ secretion by WT and MIF-deficient CD4+ T cells in presence of LPS. Data are means ± SEM from four experiments. (e) IL-2 secretion by WT and MIF-deficient CD4+ T cells in presence of LPS. Data are means ± SEM from three experiments. f) TNFα secretion by WT and MIF-deficient CD4+ T cells in presence of LPS. Data are means ± SEM from five experiments. g) Activation of MIF-deficient CD4+ T cells in presence of 10 ng/ml rMIF, and LPS. Data are means ± SEM from three experiments. h) Tlr4 mRNA expression after activation of WT and MIF-deficient CD4+ T lymphocytes: values were normalized relative to naïve cells. WT and MIF-deficient CD4+ T lymphocytes were activated with 0.5μg/ml anti-CD3 antibody. MIF-deficient CD4+ T lymphocytes were stimulated with 10 ng/ml rMIF and 0.12μg/ml anti-CD3 antibody. P > 0.05 between naïve and anti-CD3 antibody activated WT CD4+ T lymphocytes. No difference between naïve and rMIF-stimulated and anti-CD3 antibody activated MIF-deficient CD4+ T lymphocytes. p < 0.0001 between naïve and anti-CD3 antibody activated MIF-deficient CD4+ T lymphocytes. Representative of 3 different experiences. Statistical analysis of Fig. 5 is described in Table 1.