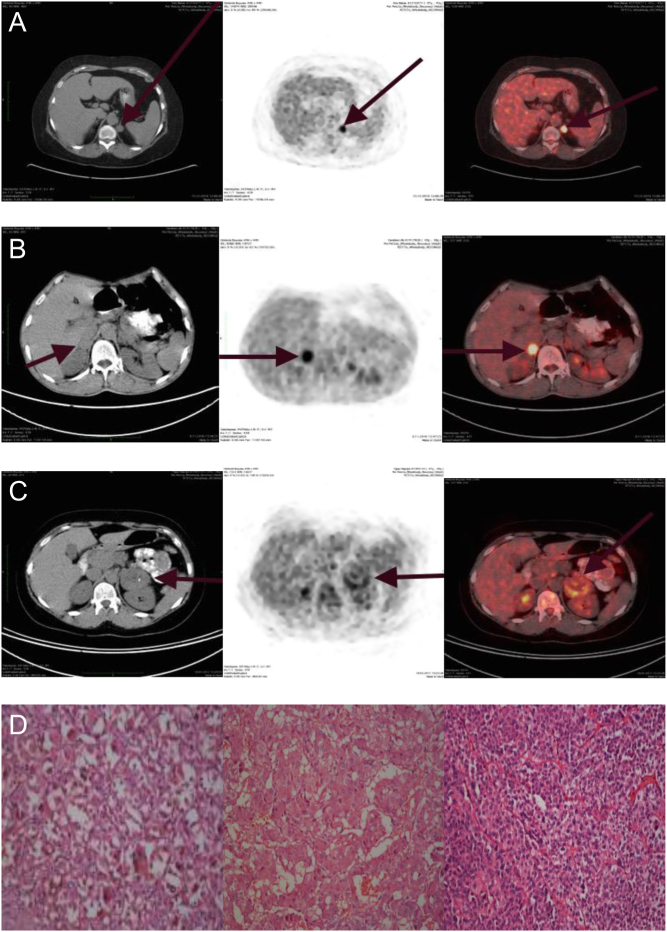
Figure 1.
(A) Coronal and axial fused 18F-FDG PET/CT images of the patient 1 adrenal glands, which was diagnosed Cushing syndrome. PET/CT showing a 1.4 × 1.7 cm left-cortisol-secreting adenoma with SUVmax 11.38. (B) Coronal and axial fused 18F-FDG PET/CT images of the patient 2 adrenal glands which were diagnosed pheochromocytoma. PET/CT showing a 3.0 × 2.1 cm right-pheochromocytoma with SUVmax 7.86. (C) Coronal and axial fused 18F-FDG PET/CT images of the patient 3 adrenal glands which were diagnosed non-functional adrenal adenoma. PET/CT showing a 52 × 50 cm- non-functional adenoma with SUVmax 4.56. (D) Adenoma cells have abundant intracytoplasmic granular lipofuscin pigment with eosinophilic cytoplasm (patient1, left side, H-E × 400). The cells of pheochromocytoma have a finely granular, basophilic cytoplasm with round-to-oval nuclei (patient 2, middle part, H-E × 200). The cells of the neoplasm have diffuse pattern with lack of clear cytoplasm (patient 3, right side, H-E × 200).

 This work is licensed under a
This work is licensed under a