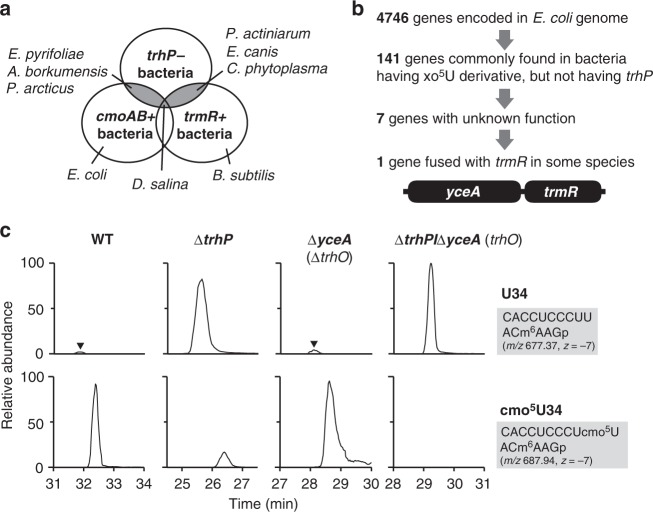
Fig. 3.
Identification of trhO responsible for tRNA hydroxylation. a Venn diagram depicts a group of organisms that have cmoAB or trmR homologs but no trhP homologs. Erwinia pyrifoliae, Alcanivorax borkumensis, and Psychrobacter arcticus harbor cmoAB but not trhP; Pontibacter actiniarum, Ehrlichia canis, and Candidatus phytoplasma harbor trmR but not trhP; and Dactylococcopsis salina has both cmoAB and trmR but not trhP. b Comparative genomics approach used to narrow down the candidate gene that bypasses ho5U34 biogenesis. In Phytophthora sojae, Phytophthora ramorum, and Phaeodatylum tricornutum, yceA and trmR are fused as a single gene. c Mass-spectrometric analysis of the wobble modification in E. coli tRNAVal1 isolated from WT (left panels), ∆trhP (middle left panels), ∆yceA (middle right panels), and ∆trhP/∆yceA (right panels) strains. XICs show anticodon-containing fragments of tRNAVal1 with U34 (upper panels) and cmo5U34 (lower panels). Black arrowheads indicate peaks corresponding to U34-containing fragments detected in the WT and ∆yceA. Sequence, m/z value, and charge state of each fragment are shown on the right