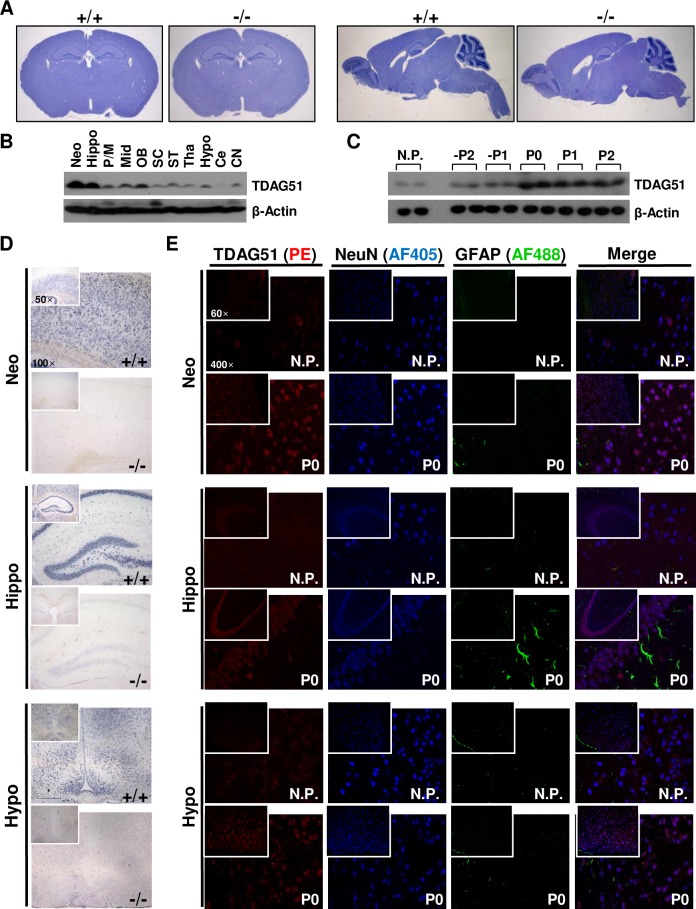
Fig 3. Expression of TDAG51 in brain tissues.
(A) TDAG51 expression in brain sections from nonpregnant female mice. Histological images of coronal brain sections (top and left panels) and sagittal brain sections (top and right panels) were obtained by hematoxylin staining. +/+, TDAG51+/+. -/-, TDAG51-/-. (B) TDAG51 expression in mouse brain tissues. TDAG51 expression in brain tissues from nonpregnant female mice was analyzed by a western blot analysis with an anti-TDAG51 antibody. β-Actin was used as a loading control. Neo, neocortex. Hippo, hippocampus. P/M, pons/medulla. Mid, midbrain. OB, olfactory bulb. SC, spinal cord. ST, stria terminalis. Tha, thalamus. Hypo, hypothalamus. Ce, cerebellum. CN, cerebral nuclei. (C) Comparison of the TDAG51 expression levels in the brain during pregnancy, parturition and postpartum periods. TDAG51 expression levels in two mice per group were analyzed by a western blot analysis using an anti-TDAG51 antibody. Nonpregnant female mice (N.P.) were used as controls. (D) In situ hybridization analysis of TDAG51 expression in mouse brain tissues. TDAG51 expression was analyzed by an in situ hybridization analysis using DIG-labeled RNA probes on P0. All images were photographed at a 50× or 100× magnification. (E) TDAG51 expression in neuronal cells in mouse brain tissues. Mouse brain tissues were stained with an anti-TDAG51 PE-conjugated, anti-GFAP Alexa Fluor 488 (AF488)-conjugated and anti-NeuN Alexa Fluor 405 (AF405)-conjugated antibodies. All images were photographed at a 60× or 400× magnification. Images from the same observed field were merged.