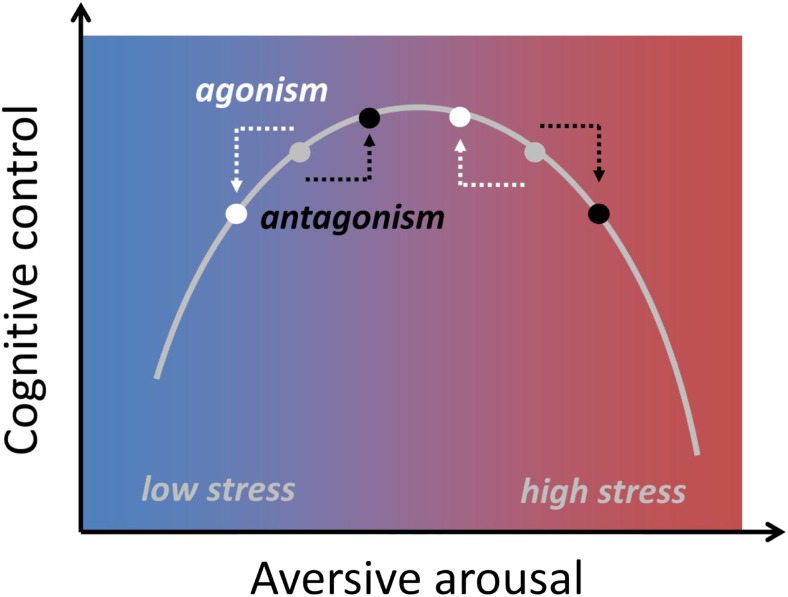
Fig. 5.
U-shaped relationship between aversive arousal and cognitive control. Opioids agonist might reduce aversive arousal (white), whereas opioid antagonist might increase it (black). According to this hypothesis, drug effects on cognition depend on the baseline level of aversive arousal, such that an opioid agonist might improve performance in high stress contexts, yet impair performance under low stress.