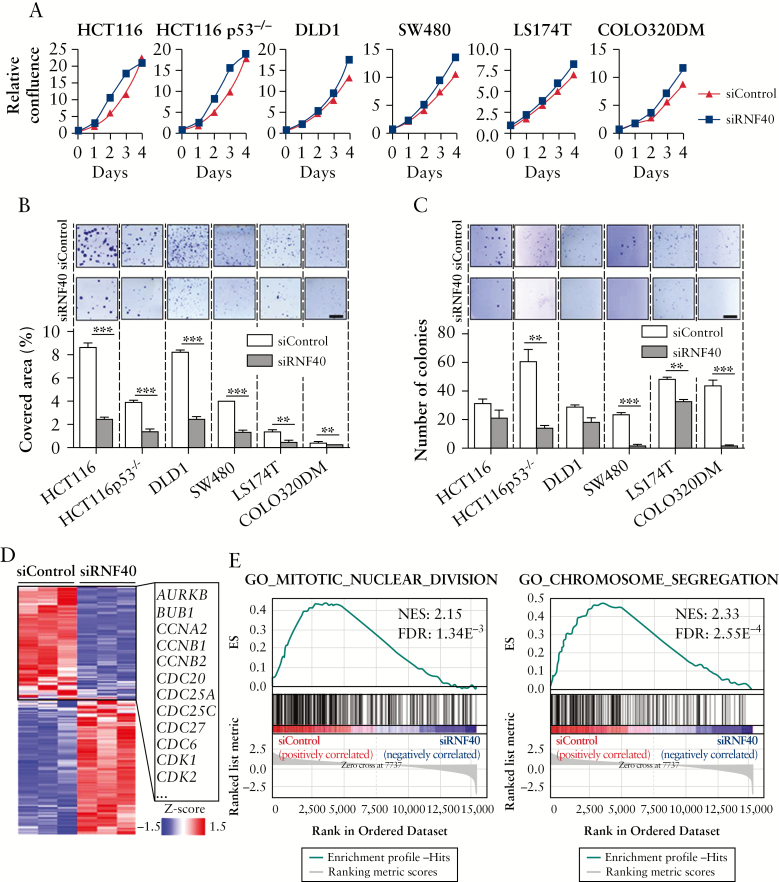
Figure 2.
RNF40 knockdown reduces tumorigenic properties of CRC cells in vitro. RNF40 levels were reduced by siRNA transfection in HCT116, HCT116 p53-/-, DLD1, SW480, LS174T, and COLO320DM cells in four independent experiments. [A] Cellular confluence was measured daily, and decreased proliferation was observed in all cell lines following RNF40 depletion [siRNF40; n = 6]. Mean ± SEM. [B] The clonogenic potential of cells was determined by allowing single cells to form colonies and quantifying the well area covered by cells [n = 3]. Upon loss of RNF40, the cells were less likely to form colonies. Scale bar: 0.5 mm. Mean ± SEM. [C] The ability of cells to grow in an anchorage-independent manner was tested using a soft agar colony formation assay [n = 3]. A reduced number of colonies was detected upon the knockdown of RNF40. Scale bar: 0.5 mm. Mean ± SEM. [D] mRNA-seq was performed to evaluate the transcriptome-wide effect of RNF40 depletion in HCT116 cells, and revealed the downregulation of several cell cycle-associated genes [n = 3]. [E] GSEA indicates that pathways related to cell division are perturbed in RNF40-depleted cells. CRC, colorectal cancer; SEM, standard error of the mean; GSEA, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis.