Fig. 8.
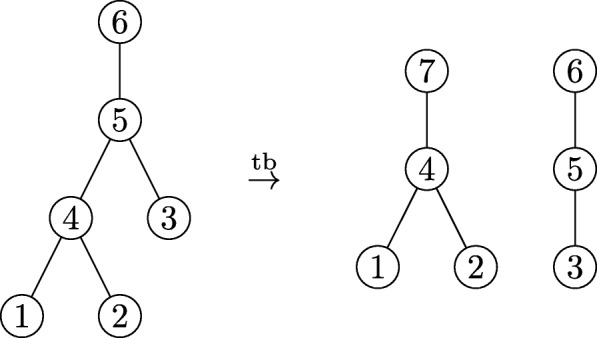
Illustration of the tree breaking function. We start off with the six-node tree T on the left. If vertex 6 is the root of T, its leaves are vertices 1, 2, and 3. When we apply the tree-breaking operation to the (5,4) edge, we obtain the forest on the right F=tb(T,(5,4)). The roots are now vertices 7 (added when we broke the tree) and 6 (the root in the initial tree) for the two trees in the forest. The leaves remain vertices 1, 2, and 3
