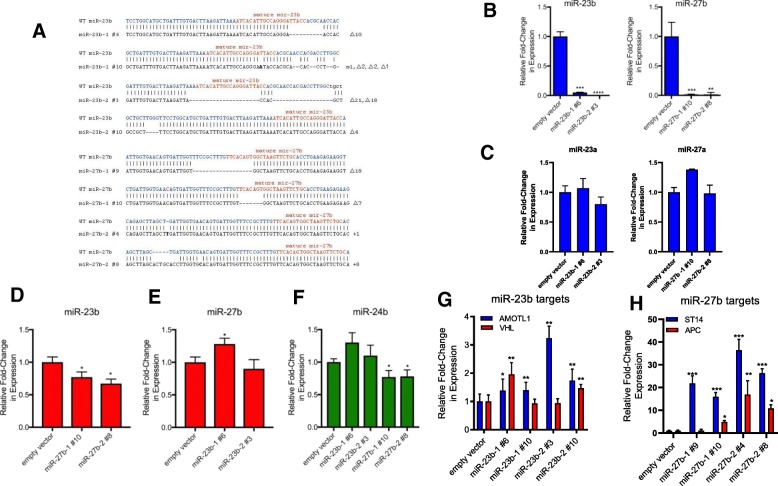
Fig. 1.
CRISPR knockout of miR-23b and miR-27b from MCF7 cells. a. Sequence alignment of indels present in miR-23b and miR-27b CRISPR knockout clones. b. qRT-PCR expression analysis of miR-23b and miR-27b in the knockout clones. c. qRT-PCR expression of homologs miR-23a and miR-27a in miR-23b and miR-27b knockout clones. miRNA expression is normalized to endogenous SNORD44 expression and relative to empty vector control cells, n = 3, ** p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.001, Student’s t-test. qRT-PCR of miR-23b expression in miR-27b knockout cells (d), miR-27b expression in miR-23b knockout cells (e), miR-24b expression in miR-23b and miR-27b knockout clones (f), normalized to SNORD44 and relative to empty vector control cells, n = 3, * p < 0.05, Student’s t-test. qRT-PCR analysis of miR-23b target genes, AMOTL1 and VHL (g) and miR-27b target genes ST14 and APC (h). Target gene expression is normalized to endogenous 36B4 expression and relative to empty vector control cells, n = 3, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, Student’s t-test