Fig. 5.
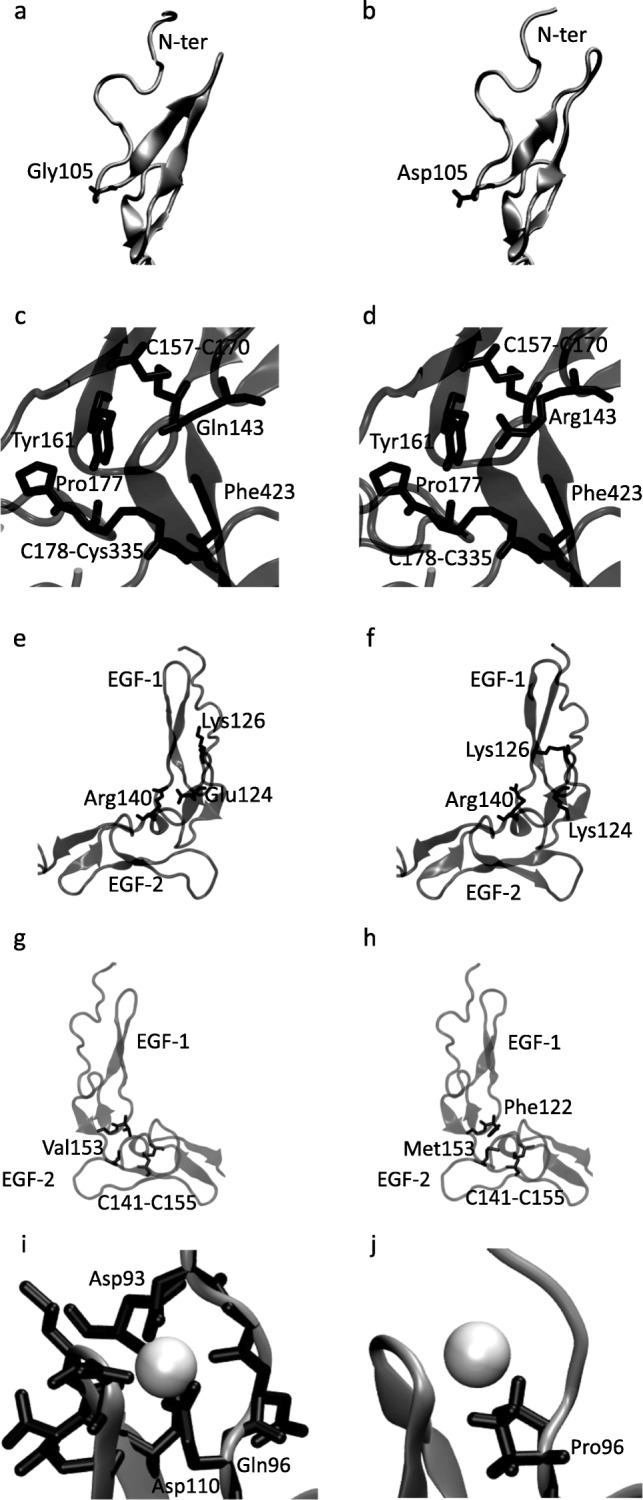
Comparison of the local environment of severe and mild mutations in the EGF domains of FIX. The protein backbone is shown in silver ribbons, interacting amino acids as a black licorice and the calcium ion as a white sphere. a, c, e, g, i correspond to wild type FIX. b, d, f, h, j correspond to mutant FIX. a Location of Gly105 in EGF-1 (from PDB ID 1PFX); the N-terminus of the domain is labeled. b Location of Asp105 in EGF-1; the N-terminus of the domain is labeled c Neighboring residues for Gln143 (from PDB ID 6MV4), labeled. d Neighboring residues for Arg143, clashing with the disulfide bond between Cys157 and Cys170, Tyr161 and Phe423. e Salt bridge between Glu124 in EGF-1 and Arg140 in EGF-2; neighboring positive residue also labeled (from PDB ID 1PFX). f Group of nearby positive charges in the Glu124Lys mutant. g Selected residues close to Val153 (from PDB ID 1PFX). h Residues that clash with Met153. i Residues coordinating the calcium ion in EGF-1; the residues that contribute their side chains are labeled (from PDB ID 1EDM). j Location of Pro96 as a first coordination shell residue for calcium
