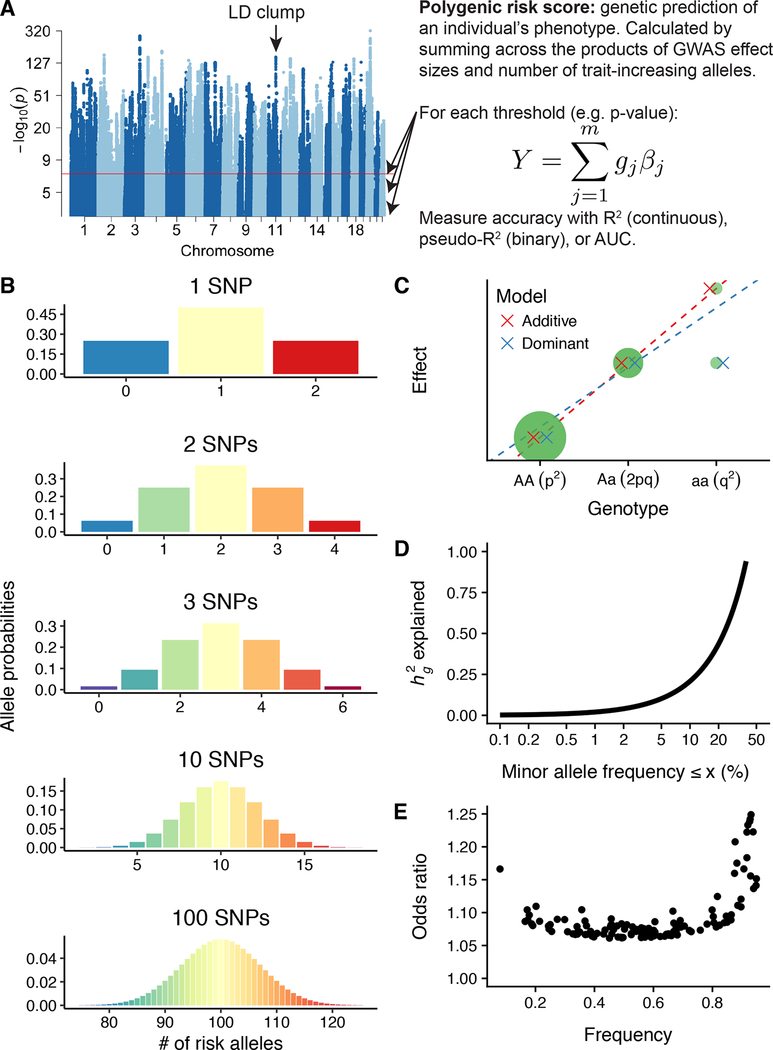
Figure 2. Normal genetic risk in a population with an additive genetic architecture.
A) Definition and illustration of polygenic risk score calculation. Using a set of existing GWAS summary statistics, the polygenic risk score is computed in a target cohort as where j is a SNP in m independent SNPs associated with the phenotype of interest, g is the number of trait-increasing alleles for a particular SNP, and β is the corresponding GWAS effect size estimate. An LD clump is an associated locus with one or few causal loci but a linkage peak of associated variants due to LD correlation in the region. The signal-to-noise ratio can be tuned to maximize prediction accuracy in a target cohort by modifying the maximum p-value threshold for SNP inclusion. B) Large numbers of SNPs contributing to complex traits can be modeled accurately with genetic liability as a normal distribution. Here, we demonstrate this by showing the genetic risk distribution for increasing numbers of SNPs with an allele frequency of 0.5 (although normality is expected regardless of allele frequency when larger numbers of SNPs are causal). The best-powered GWAS of complex traits such as height, schizophrenia, and educational attainment have identified hundreds to thousands of independent, genome-wide significant loci. This phenomenon can be explained by the central limit theorem as demonstrated previously (107). C) Additive GWAS regression models tend to work well for genetic associations across a range of allele frequencies, even in the presence of dominance. D) Previous work in the UK Biobank has demonstrated that across 25 complex traits and diseases, most of the heritable variation in complex traits can be explained by common variants (e.g., ≥ 5% allele frequency). While the exact proportion can vary, the curve illustrates h2 = 2*p*(1-p)α, where α = −0.38 ± 0.02 across complex traits (108). E) A previous GWAS of schizophrenia identified 128 independent genome-wide significant loci, shown here (11). These loci illustrate a relationship between frequency and corresponding odds ratios, in which lower frequency variants can have larger effect sizes, reflecting the impact of natural selection on genetic architecture.