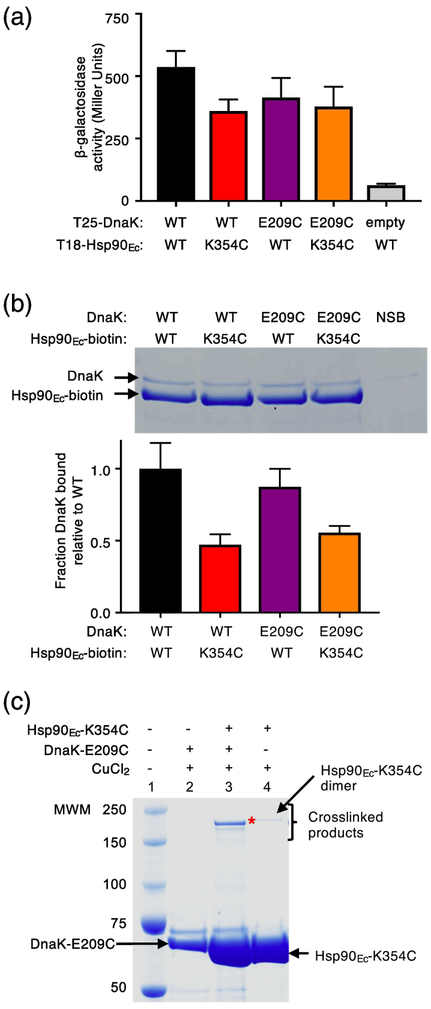
Fig. 2.
Specific crosslinking of a pair of Hsp90Ec and DnaK residues important for interaction. (a) The in vivo interaction between Hsp90Ec wild-type or K354C and DnaK wild-type or E209C was monitored using a bacterial two-hybrid system that measured beta-galactosidase activity in liquid culture. β-galactosidase activity is shown as mean ± SEM (n=3). (b) The in vitro interaction between biotinylated Hsp90Ec wild-type or K354C and DnaK wild-type or E209C (4 μM each) was determined using a pull-down assay in the presence of L2, CbpA and ATP as described in Materials and Methods and analyzed by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining. DnaK wild-type or E209C associated with biotinylated Hsp90Ec wild-type or K354C was quantified using densitometry as described in Materials and Methods and is shown as a bar graph. For each lane of the gel the amount of DnaK was corrected for non-specific binding (NSB) and then was normalized to Hsp90Ec-biotin and the ratio of DnaK mutant to wild-type is plotted as the mean ± SEM (n=6). (c) Hsp90Ec-K354C and DnaK-E209C were treated with CuCl2 (~2 Å linker) alone and in a mixture together and covalent bond formation was monitored by SDS-PAGE followed by Coomassie blue staining. (*) indicates crosslinked product of interest. A small amount of a slowly migrating species was likely the covalently linked Hsp90Ec-K354C dimer, since it was observed in reactions with and without Ssa1 (lanes 3 and 4). In (c), the gel shown is representative of at least three independent experiments.